- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.
Global competition in aerospace and automotive innovation hinges on agility, and 3D printing is delivering results that British manufacturers are watching closely. Over 60% of advanced engineering firms now rely on additive manufacturing to produce complex prototypes in days, not weeks. For engineers and product designers facing tight deadlines and growing design challenges, understanding core 3D printing principles offers a direct path to faster prototyping and shorter production timelines.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Core Principles of 3D Printing | Additive manufacturing revolutionises production by enabling complex designs through layer-by-layer construction. Various technologies like FDM, SLA, and SLS each offer unique advantages for different project needs. |
| China's Leadership in 3D Printing | China is emerging as a leader in additive manufacturing, with rapid adoption in sectors like aerospace and automotive. Significant advancements in technology are driving industrial innovation and efficiency. |
| Business Impact in Key Sectors | 3D printing enhances design flexibility and cost efficiency in aerospace and automotive sectors, reducing production times and material waste. Companies can innovate faster with complex geometries and customised components. |
| Future Directions | The focus is shifting from prototyping to full-scale production, with an emphasis on smart manufacturing and sustainability. Investing in workforce training and cross-disciplinary skills will be crucial for adapting to the evolving landscape. |
Additive manufacturing transforms digital designs into physical objects through layer-by-layer construction, representing a fundamental shift from traditional manufacturing techniques. Complex geometric possibilities enable engineers and designers to create intricate structures previously impossible with conventional methods.
The core principles of 3D printing revolve around converting digital 3D models into physical components using various technologies like Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and Selective Laser Sintering (SLS). These techniques share a common approach: transforming computer-aided design (CAD) files into tangible objects by systematically depositing material layer by precise layer. Each technology offers unique advantages, allowing manufacturers to select optimal processes based on specific project requirements such as material properties, resolution, and structural complexity.
Key technologies within 3D printing services include:
Pro tip: When selecting a 3D printing service, always request material compatibility tests and dimensional accuracy reports to ensure your prototype meets precise engineering specifications.
China has emerged as a global leader in additive manufacturing, with significant advancements across multiple 3D printing technologies. Major research institutions are driving technological innovation in powder bed fusion, material extrusion, and photopolymerisation techniques, positioning the country at the forefront of manufacturing transformation.

The primary 3D printing technologies currently prominent in China include Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), and Digital Light Processing (DLP). Rapid industrial adoption characterises these technologies, particularly in strategic sectors like aerospace, automotive, and advanced manufacturing. Chinese manufacturers have demonstrated remarkable capabilities in developing sophisticated additive manufacturing processes that enable complex geometrical structures and high-precision component production.
Key 3D printing technologies in the Chinese market encompass:
Here is a comparison of major 3D printing technologies relevant in China:
| Technology | Key Material | Typical Industry Use | Notable Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) | Thermoplastic filament | Automotive prototyping | Cost-effective for models |
| Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | Metal powder | Aerospace parts production | Produces strong metal items |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | Photopolymer resin | High-precision component | Excellent surface finish |
| Material Jetting | Photopolymer and wax | Custom, multi-colour objects | Simultaneous colour results |
| Powder Bed Fusion | Metal and polymers | Complex, functional parts | Enables multi-material use |
Pro tip: When exploring 3D printing technologies in China, request comprehensive material compatibility reports and verify the manufacturer's quality certification to ensure optimal performance and reliability.
Additive manufacturing has revolutionised business strategies in aerospace and automotive sectors, delivering unprecedented engineering capabilities. Transformative manufacturing technologies are enabling companies to dramatically reduce production costs, accelerate design iterations, and create increasingly complex component geometries that were previously impossible with traditional manufacturing methods.
In the aerospace industry, 3D printing enables lightweight component production that significantly reduces aircraft weight and improves fuel efficiency. Automotive manufacturers are leveraging these technologies to develop intricate parts with reduced material waste and enhanced performance characteristics. Complex geometries and material customisation are driving innovation, allowing engineers to reimagine traditional design constraints and develop more sophisticated, efficient manufacturing processes.
Key business advantages of 3D printing in these industries include:
Pro tip: Invest in comprehensive training programmes to develop internal additive manufacturing expertise, ensuring your organisation can effectively leverage these transformative technologies.
The 3D printing landscape in China is experiencing a transformative evolution, driven by strategic technological advancements and governmental support. Material innovation and digital integration are reshaping the manufacturing ecosystem, enabling unprecedented capabilities in industrial production and design flexibility.
Emergent trends are characterised by a significant shift from traditional prototyping towards full-scale manufacturing across multiple sectors. Technological adoption with Industry 4.0 integration is accelerating, with artificial intelligence and internet of things (IoT) technologies playing crucial roles in advancing additive manufacturing capabilities. Chinese manufacturers are increasingly focusing on multi-material printing techniques, sustainable manufacturing practices, and developing sophisticated automation systems.
Key trends transforming China's 3D printing landscape include:
Pro tip:Continuously monitor technological developments and invest in upskilling your workforce to effectively leverage emerging 3D printing capabilities and maintain competitive advantage.
Chinese 3D manufacturing faces significant obstacles that could impede technological advancement and industrial adoption. Material limitations and process instability represent critical challenges that demand comprehensive technological intervention and strategic research investment.
Intellectual property protection remains a paramount concern, with complex regulatory environments creating uncertainties for manufacturers. Technological risks and standardisation gaps significantly impact the industry's global competitiveness and potential for sustainable growth. These challenges extend beyond technical constraints, encompassing broader economic and regulatory frameworks that require nuanced policy approaches.
Key challenges in Chinese 3D manufacturing include:
The following table summarises main challenges and strategic responses in Chinese 3D manufacturing:
| Challenge | Impact on Industry | Recommended Strategic Response |
|---|---|---|
| Immature materials | Limits part reliability | Invest in R&D partnerships |
| Quality inconsistency | Creates product defects | Develop robust quality management |
| Weak IP protection | Inhibits innovation | Strengthen internal legal processes |
| High production cost | Reduces competitiveness | Scale automation to lower expenses |
| Regulation gaps | Introduces uncertainty | Engage with industry standard bodies |
Pro tip: Develop robust internal quality management systems and continuously invest in research partnerships to mitigate technological risks and enhance manufacturing capabilities.
The trajectory of 3D printing in China is rapidly evolving from traditional prototyping towards comprehensive manufacturing solutions. Smart factory implementations will transform industrial processes, enabling more sophisticated and flexible production capabilities that transcend conventional manufacturing limitations.
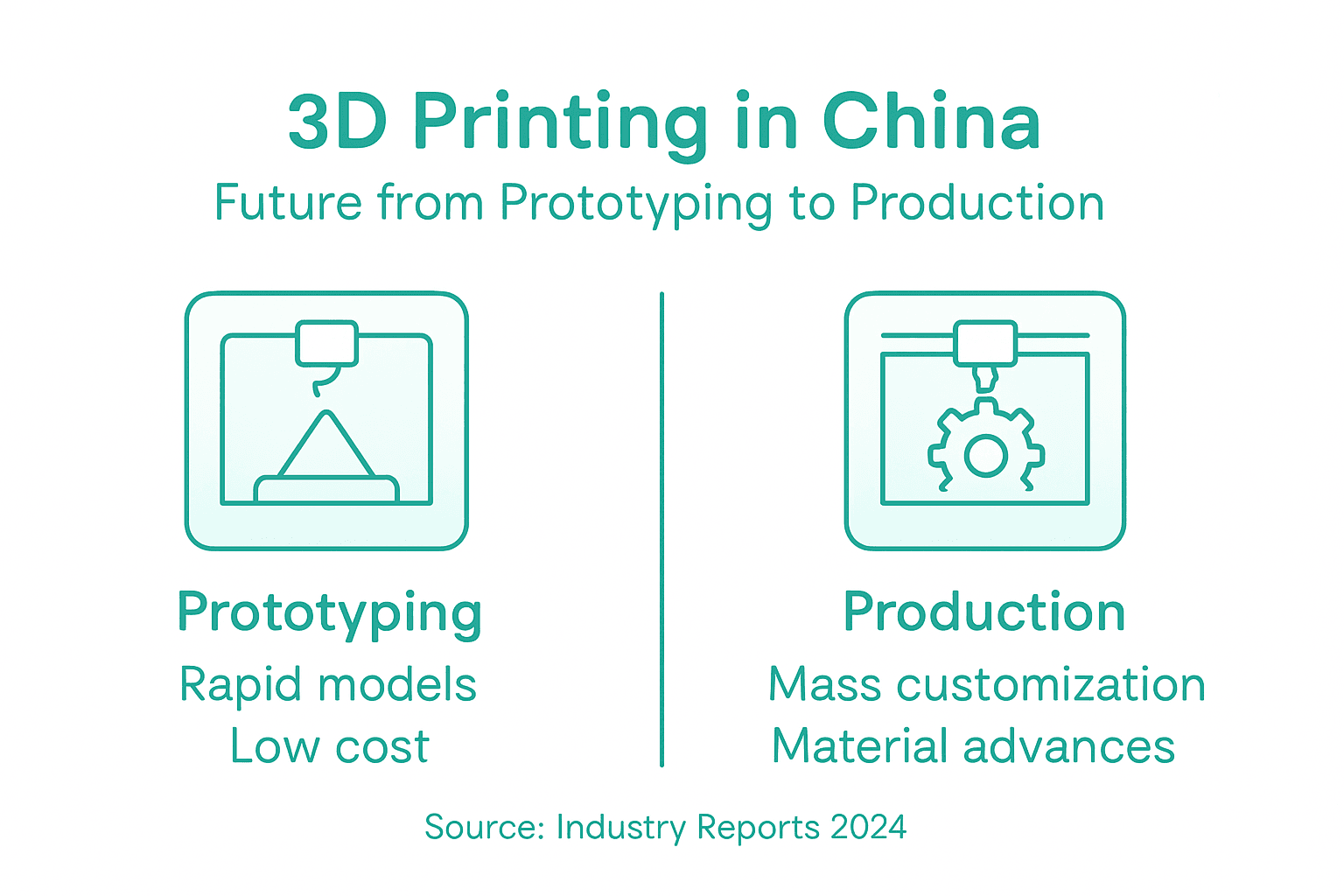
Advances in multi-material printing and large-scale additive manufacturing are driving substantial changes across industrial sectors. Expanded materials portfolios and automation technologies are creating unprecedented opportunities for customised, efficient production platforms. These developments suggest a fundamental restructuring of manufacturing paradigms, with 3D printing transitioning from a supplementary technology to a core industrial strategy.
Key predictions for future 3D printing development include:
Pro tip: Invest strategically in cross-disciplinary training programmes that blend digital design, materials science, and advanced manufacturing skills to prepare your workforce for the evolving technological landscape.
Navigating the challenges of material limitations, quality inconsistency, and the need for rapid prototyping highlighted in the latest trends of Chinese 3D printing can feel overwhelming. You want precision engineering, cost-effective solutions, and the assurance that your additive manufacturing projects meet exacting standards. WJ Prototypes specialises in turning these goals into reality by offering advanced 3D printing technologies such as SLA, SLS, and DMLS alongside traditional fabrication methods tailored for aerospace, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Ready to accelerate your product development with a trusted partner who understands China's dynamic manufacturing landscape? Explore how our comprehensive suite of services can overcome common obstacles and deliver high-quality, rapid turnaround prototyping with a focus on reliability and innovation. Take the next step today by visiting WJ Prototypes or discover more about our advanced manufacturing solutions designed to keep you ahead in a competitive market.
The primary technologies in 3D printing include Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Digital Light Processing (DLP). Each technology has its specific applications and advantages, such as cost-effectiveness and precision.
3D printing has significantly revolutionised the aerospace and automotive sectors by enabling lightweight component production, reducing material waste, and allowing for intricate designs that were impossible with traditional methods. This leads to improved fuel efficiency and enhanced performance characteristics.
Key trends in 3D printing include material innovation, integration with AI and IoT technologies, a shift toward industrial-scale manufacturing, and a focus on sustainable practices. These developments suggest a transformative evolution in manufacturing capabilities.
Challenges in 3D manufacturing include immature materials that limit part reliability, quality inconsistencies that lead to defects, weak intellectual property protections, high production costs, and regulatory gaps that create uncertainty for manufacturers.
Global B2B Demand for 3D Printed Parts - WJ Prototype
On-Demand 3D Printing Services for Your Business Needs
3D Printing Price In China - Key Insights on Bulk Order Pricing
Medical 3D Printing in China | Benefits For Global Companies