- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.


Cost pressures are pushing North American automotive engineers to rethink traditional prototyping, especially as British and Chinese manufacturing approaches redefine industry benchmarks. With development expenses slashed by up to 60% in leading Asian facilities, firms targeting faster vehicle design cycles can no longer afford outdated workflows. This overview breaks down modern prototyping processes, technologies, and competitive advantages to help you maximise development speed while remaining resource-efficient in a global automotive market.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Importance of Prototyping | Automotive prototyping is crucial for validating design feasibility and refining innovations before full-scale production. |
| Types of Prototypes | Different types of prototypes, such as concept and functional prototypes, serve specific purposes in the development process. |
| Technological Advancements | Modern prototyping leverages advanced technologies like 3D printing and intelligent simulations to enhance precision and speed. |
| China's Competitive Edge | China's automotive prototyping benefits from rapid innovation, cost efficiency, and robust supply chain integration, positioning it as a global leader. |
Automotive prototyping represents a sophisticated engineering process that transforms conceptual vehicle designs into tangible, functional representations. These pre-production models are critical for automotive manufacturers to validate design feasibility, test performance parameters, and refine technological innovations before committing to full-scale production. Comprehensive prototyping strategies enable engineers to systematically evaluate design concepts across multiple dimensions.
The automotive prototyping process typically involves several interconnected stages that transform abstract ideas into physical models. Initially, design engineers develop digital 3D models using advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software, allowing precise visualisation and preliminary simulation. These digital blueprints then transition into physical prototypes through technologies like 3D printing, CNC machining, and injection moulding. Product development lifecycles demonstrate that prototyping bridges conceptual design and validation, enabling manufacturers to assess function, performance, and manufacturability with remarkable precision.
Modern automotive prototyping encompasses multiple sophisticated techniques tailored to different development objectives. Rapid prototyping methods like additive manufacturing enable quick iterations, while more advanced techniques such as functional prototyping create near-production quality models that closely simulate real-world performance. These approaches allow automotive engineers to test critical components including drivetrain systems, electrical architectures, and structural integrity under simulated conditions. The iterative nature of prototyping means each model refines understanding, reduces potential design flaws, and accelerates the path from concept to production.
Pro Tip: Prototype Selection Strategy: Choose prototyping techniques based on specific development stage requirements, balancing speed, cost, and fidelity to maximise engineering insights and minimise potential design risks.
Automotive prototypes encompass a diverse range of representations designed to address specific engineering challenges and development objectives. Comprehensive prototype classifications reveal multiple strategic variations that enable automotive engineers to systematically evaluate and refine vehicle designs through targeted model development.
The primary categories of automotive prototypes include concept prototypes, which visualise initial design ideas, and functional prototypes that demonstrate specific mechanical or technological capabilities. More advanced variations like pre-production prototypes closely simulate final manufacturing specifications, allowing comprehensive performance testing. Contemporary prototyping methods distinguish between different prototype approaches based on critical parameters such as:
Each prototype variation serves a unique purpose in the automotive development workflow, enabling engineers to progressively validate design concepts, test technological innovations, and mitigate potential manufacturing risks. The iterative nature of these prototyping approaches allows manufacturers to refine vehicle designs with increasing precision, ultimately delivering more sophisticated and reliable automotive solutions.
The following table summarises the key types of automotive prototypes and their strategic business impact:
| Prototype Type | Primary Purpose | Typical Use Case | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Concept Prototype | Visualise design intent | Early-stage evaluation | Informs go/no-go decisions |
| Functional Prototype | Validate technical feasibility | Testing mechanical systems | Reduces risk of design flaws |
| Pre-production | Simulate final specifications | Manufacturing process trials | Streamlines production readiness |
| Subsystem Prototype | Assess individual components | Isolated part testing | Accelerates innovation on features |
Pro Tip: Prototype Progression Strategy: Select prototype variations strategically by matching each model's complexity and purpose to specific development stage requirements, ensuring efficient resource utilisation and comprehensive design validation.
Modern automotive prototyping has undergone a revolutionary transformation, driven by cutting-edge technological innovations that fundamentally reshape design and development processes. Emerging technologies in rapid prototyping have dramatically accelerated automotive engineering capabilities, introducing unprecedented precision and efficiency into the product development lifecycle.

Three primary technological domains are fundamentally reshaping automotive prototyping: advanced digital technologies, sophisticated manufacturing techniques, and intelligent simulation platforms. 3D printing and additive manufacturing stand at the forefront, enabling engineers to create complex geometries and functional prototypes with remarkable speed and accuracy. Computer-aided design (CAD) software now integrates seamlessly with simulation tools, allowing real-time performance analysis and virtual testing before physical model creation. Digital and green transitions are driving significant changes in prototyping methodologies, emphasising sustainability and technological integration.
Key technological enablers in modern automotive prototyping include:
These technological advances not only accelerate prototype development but also dramatically reduce costs, enhance design flexibility, and support more sustainable engineering practices. The convergence of digital simulation, advanced materials, and intelligent manufacturing is transforming automotive prototyping from a linear process into a dynamic, interconnected ecosystem of innovation.
Pro Tip: Technology Integration Strategy: Continuously invest in cross-platform training for engineering teams, ensuring seamless adoption of emerging prototyping technologies and maintaining a competitive technological edge.
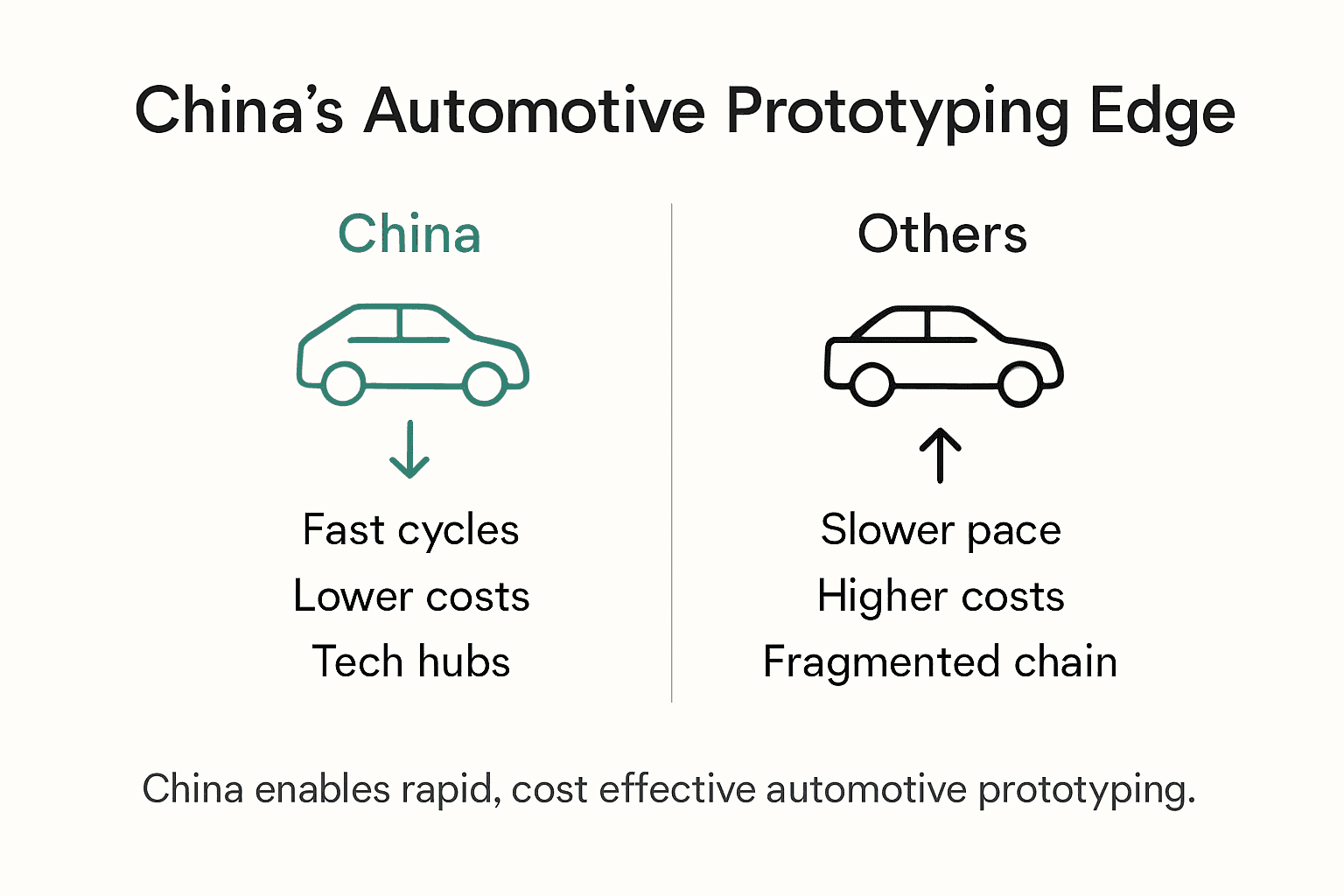
China's automotive prototyping landscape has emerged as a global powerhouse, distinguished by its unprecedented combination of technological infrastructure, manufacturing agility, and strategic innovation capabilities. China's innovation ecosystem represents a transformative approach to automotive engineering, characterised by rapid adaptation, extensive supplier networks, and an extraordinary capacity for technological iteration.
The core advantages driving China's automotive prototyping leadership stem from multiple interconnected factors. Technological infrastructure plays a pivotal role, with massive investments in advanced manufacturing technologies, artificial intelligence, and sophisticated engineering capabilities. The country's dense industrial clusters enable unprecedented collaboration between research institutions, manufacturing facilities, and technological innovators. Automotive engineers benefit from an ecosystem that supports rapid design-to-prototype transitions, allowing for significantly faster product development cycles compared to traditional manufacturing environments.
Key competitive advantages for Chinese automotive prototyping include:
Moreover, China's approach to automotive prototyping transcends traditional manufacturing paradigms by embracing a holistic, technology-driven strategy. The combination of robust digital infrastructure, skilled engineering talent, and supportive regulatory frameworks creates a uniquely dynamic environment for automotive innovation. This ecosystem allows automotive manufacturers to experiment, iterate, and deploy new technologies with remarkable efficiency and speed.
Pro Tip: Strategic Adaptation Strategy: Develop robust cross-functional teams capable of integrating multiple technological disciplines, enabling faster response to emerging automotive design and engineering challenges.
The global automotive prototyping landscape reveals profound differences between China and other manufacturing regions, with China demonstrating remarkable strategic advantages. Structural factors in automotive manufacturing highlight how China's unique approach to technological development and industrial policy has fundamentally transformed its competitive positioning in the global market.
Comparing China with traditional manufacturing powerhouses like the United States, Germany, and Japan unveils nuanced differences in prototyping strategies. Technological knowledge transfer emerges as a critical distinguishing factor, with China's collaborative industrial model enabling accelerated learning and capability development. Unlike Western regions that traditionally maintained stricter technological boundaries, China has systematically cultivated an ecosystem of rapid technological adaptation, particularly through strategic joint ventures and aggressive skills development programmes.
Key comparative dimensions between China and other manufacturing regions include:
Electric vehicle prototyping evolution further illustrates China's distinctive approach, with the country rapidly scaling infrastructure and integration capabilities that outpace traditional automotive manufacturing centres. This ecosystem approach enables Chinese manufacturers to compress development timelines, reduce costs, and accelerate technological iterations in ways that challenge established global competitors.
Below is a comparison of major automotive prototyping regions, highlighting their distinctive strengths:
| Region | Innovation Speed | Cost Efficiency | Regulatory Flexibility | Talent Development Approach |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| China | Exceptionally rapid | Very high | Highly adaptive | Integrated, aggressive |
| Germany | Methodical, high quality | Moderate | Structured, conventional | Specialised, rigorous |
| USA | Fast for niche segments | Moderate to high | Strict, well-defined | Portfolio and institutional |
| Japan | Incremental, reliable | Moderate | Conservative, process-focused | Lifelong, company-based |
Pro Tip: Competitive Benchmarking Strategy: Continuously monitor and analyse China's automotive prototyping methodologies to identify potential efficiency improvements and technological innovation strategies applicable to your own manufacturing processes.
Automotive firms engaging with China's prototyping ecosystem unlock substantial financial and operational advantages that fundamentally transform traditional product development approaches. Cost savings and operational efficiencies represent more than mere economic benefits—they constitute a strategic transformation of automotive research and development methodologies.
Integrated manufacturing networks enable unprecedented economic advantages for automotive firms. By leveraging China's comprehensive industrial infrastructure, companies can dramatically reduce prototype development timelines and associated expenses. Unlike traditional Western manufacturing models that emphasise sequential development processes, Chinese ecosystems support simultaneous testing, iteration, and refinement, creating a more dynamic and cost-effective environment for automotive innovation.
Key financial and operational benefits include:
China's manufacturing landscape demonstrates how integrated supply chains and competitive economic structures create unique advantages for automotive firms. These benefits extend beyond immediate cost reductions, offering strategic capabilities that enable more responsive, innovative product development approaches that can fundamentally reshape global automotive competitiveness.
Pro Tip: Strategic Partnership Strategy: Develop collaborative relationships with Chinese prototyping ecosystems, focusing on knowledge transfer and technological integration to maximise operational and financial advantages.
The article highlights the unique advantages China offers in automotive prototyping, including rapid innovation cycles, cost efficiency, and integrated supply chains. These factors address critical challenges such as reducing development time and mitigating design risks while balancing quality with affordability. Automotive innovators seeking fast yet reliable prototyping solutions must leverage cutting-edge technologies like SLA, SLS, and CNC machining alongside a network that supports agile iteration and production readiness.
At WJ Prototypes, we specialise in bringing these unique strengths to your doorstep. Our comprehensive additive manufacturing and traditional fabrication services fully embrace China’s hyper-adaptive manufacturing ecosystem, enabling you to accelerate your product development with precision engineering and cost-effective methods. Explore our capabilities in rapid prototyping that align perfectly with the article’s emphasis on technological integration and speed. Don't let the complexity of automotive prototyping slow your progress. Visit WJ Prototypes today to get an instant quote and partner with a global leader in prototyping innovation.
The automotive prototyping process typically includes stages such as developing digital 3D models using CAD software, creating physical prototypes through technologies like 3D printing and CNC machining, and conducting performance testing to validate design concepts before production.
There are several types of automotive prototypes, including concept prototypes for visualising initial designs, functional prototypes for testing technical feasibility, pre-production prototypes for simulating final manufacturing specifications, and subsystem prototypes that focus on individual vehicle components.
Modern technologies such as 3D printing, advanced robotics, and machine learning have accelerated the automotive prototyping process, providing tools for precise modelling, rapid iterations, and enhanced performance testing, significantly reducing costs and development time.
China benefits from extensive manufacturing infrastructure, rapid innovation cycles, cost-effective prototyping, and strong government support for technological advancement, enabling automotive firms to achieve faster product development and lower costs compared to traditional manufacturing powerhouses.