- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.


Every year, the manufacturing sector relies on injection moulding to deliver billions of precise components to consumers and industries worldwide. This process accounts for over 70% of all plastic products made today, making it a true powerhouse behind everyday items and specialised equipment alike. Understanding injection moulding matters for anyone interested in how complex parts are shaped so quickly and consistently. Here, you will learn the essentials of how this remarkable method works and why it remains at the heart of modern british manufacturing.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Injection Moulding Process | The process consists of five key stages: material preparation, plasticisation, injection, cooling, and ejection, each crucial for achieving optimal production quality. |
| Types of Injection Moulding | Different techniques, such as standard injection, overmoulding, and insert moulding, cater to specific manufacturing needs, expanding design possibilities. |
| Material Selection | The choice of thermoplastics, such as nylon and ABS, significantly impacts the performance and durability of the final products. |
| Industrial Applications | Injection moulding is widely used in automotive, medical, and electronics sectors, providing high production rates and consistent part quality. |
Injection moulding is a sophisticated manufacturing technique that enables the mass production of complex parts with remarkable precision and efficiency. According to Wikipedia, this process involves "injecting molten material into a mould" to create intricate components, primarily used in plastic manufacturing.
The core mechanism of injection moulding centres on transforming raw material into a finished product through a carefully controlled sequence of steps. As detailed by CSPlast, the process cycle encompasses four critical stages:
Typically, this entire process can transpire within an impressively short timeframe ranging from 2 seconds to several minutes, demonstrating the method's exceptional speed and efficiency. For engineers and designers seeking a reliable, repeatable manufacturing technique, understanding part design considerations becomes crucial in achieving optimal results.
The versatility of injection moulding makes it a cornerstone technology across numerous industries.
Whether creating intricate medical devices, robust automotive components, or precision electronic housings, this process offers unparalleled capability to transform raw materials into complex, functional parts with extraordinary consistency and accuracy.
Injection moulding represents a complex manufacturing process with multiple precise stages that transform raw materials into finished components. Understanding these stages is crucial for engineers and designers seeking optimal manufacturing outcomes.
The injection moulding process typically comprises five interconnected stages:
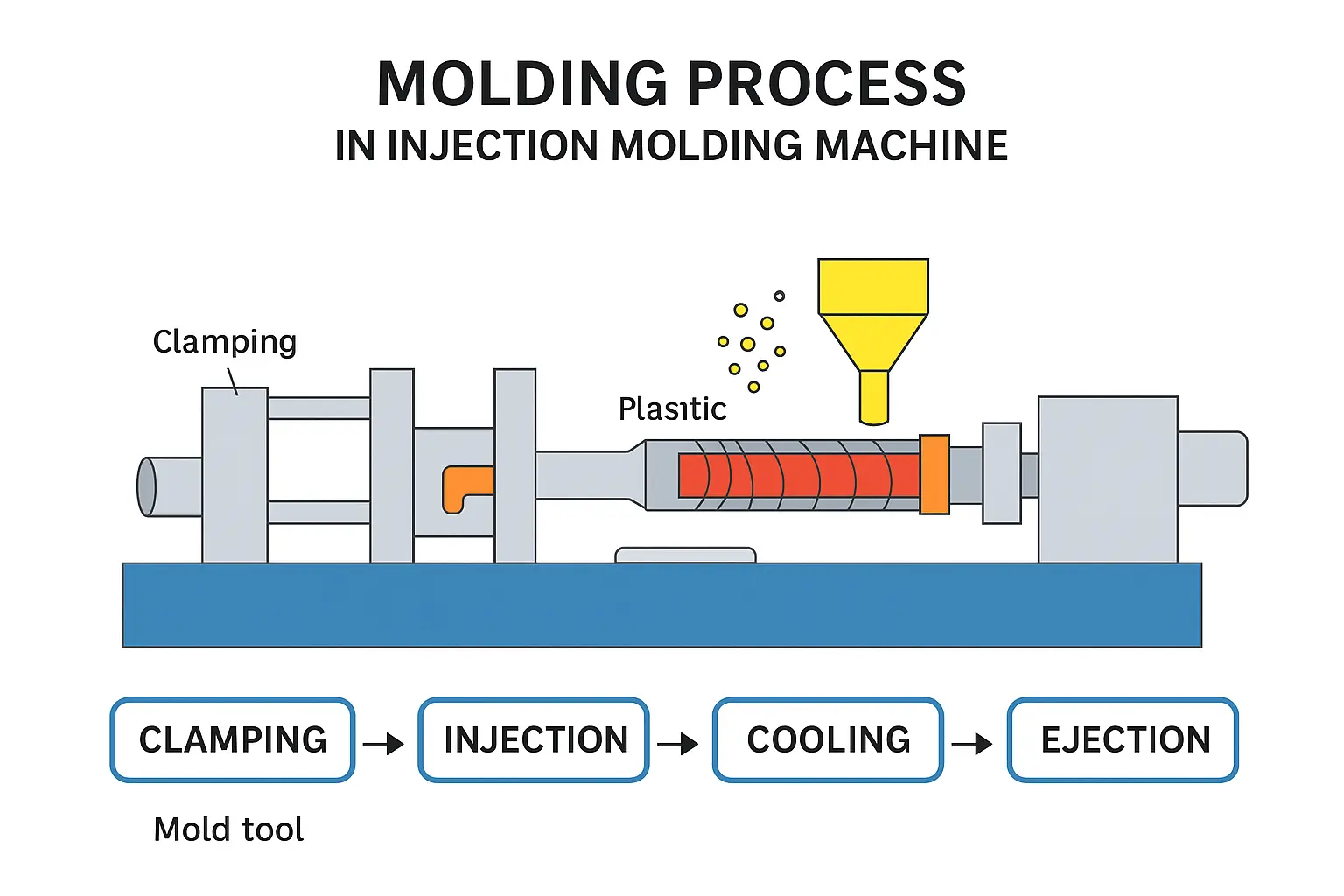
For engineers seeking deeper insights into material selection, exploring comprehensive injection moulding materials becomes essential.
Each stage demands meticulous attention to detail, with even minor variations potentially impacting final product quality, dimensional accuracy, and mechanical performance.

Injection moulding encompasses a diverse range of techniques, each designed to address specific manufacturing challenges and product requirements. According to Wikipedia, the primary types of injection moulding include standard injection moulding, overmoulding, and insert moulding, each offering unique capabilities for creating complex components.
For manufacturers seeking deeper insights into advanced manufacturing techniques, understanding precision injection moulding services becomes essential for selecting the most appropriate technique for specific product requirements.
Each injection moulding type presents distinct advantages, enabling engineers to create sophisticated, multi-functional components that meet increasingly complex design specifications. The selection depends on material properties, intended product functionality, and manufacturing constraints, making it crucial to carefully evaluate the specific requirements of each project.
Injection moulding relies on a sophisticated selection of materials that define the performance, durability, and functionality of manufactured components. According to Wikipedia, the most prevalent materials include thermoplastics such as nylon, polycarbonate, polypropylene, polystyrene, and ABS, each offering unique mechanical and thermal properties.
Manufacturers seeking comprehensive insights into material selection can explore detailed injection moulding material guides to make informed decisions about polymer selection for specific applications.
The strategic selection of injection moulding materials demands a nuanced understanding of each polymer's unique characteristics, ensuring optimal performance across diverse industrial environments from aerospace to medical device manufacturing.
Injection moulding has emerged as a transformative manufacturing technology across multiple industrial sectors. According to Wikipedia, this versatile process is extensively used to produce a wide range of parts, from intricate small components to entire automotive body panels, demonstrating its remarkable adaptability and precision.
Engineers and procurement managers seeking comprehensive manufacturing solutions can explore precision injection moulding companies in china to understand how advanced manufacturing techniques can transform product development strategies.
The strategic implementation of injection moulding technologies enables manufacturers to achieve unprecedented levels of efficiency, quality, and design complexity across diverse industrial landscapes, from automotive engineering to medical device production.
Injection moulding presents a complex landscape of manufacturing considerations, balancing technological capabilities with economic constraints. According to Wikipedia, while this process offers substantial advantages, it simultaneously introduces significant challenges, particularly around initial investment and design complexity.
Manufacturers seeking comprehensive insights can explore alternative manufacturing processes to determine the most appropriate technology for specific project requirements.
Ultimately, selecting the optimal manufacturing approach demands a nuanced understanding of project-specific parameters, balancing technical feasibility, economic constraints, and desired output quality across different production methodologies.
Mastering the intricacies of injection moulding calls for not only deep understanding of material selection, process stages, and manufacturing challenges but also access to reliable production partners who can deliver fast, accurate, and cost-effective results. Whether your project demands complex geometries, tight tolerances, or low to medium volume runs, it is vital to work with a manufacturer that comprehends these exact needs and can guide you through design optimisation and material choices.
At WJ Prototypes, we specialise in precision injection moulding services tailored to help you overcome common pain points like high initial tooling costs and design complexity. Our experienced engineers use advanced technologies alongside a wide material selection to bring your concepts to life swiftly without compromising quality. Ready to move from design to market with confidence? Discover how our precision injection moulding services and comprehensive manufacturing solutions can accelerate your product development journey. Start your project’s success with a fast and competitive quote today at WJ Prototypes.
Injection moulding is a manufacturing technique that involves injecting molten material into a mould to create complex and precise parts, primarily used in plastic manufacturing.
The injection moulding process includes five key stages: material preparation, plasticisation, injection, cooling, and ejection. Each stage plays an essential role in ensuring the quality and accuracy of the finished product.
Common materials used in injection moulding include thermoplastics such as nylon, polycarbonate, polypropylene, polystyrene, and ABS. Each has unique mechanical and thermal properties suitable for different applications.
Injection moulding offers several benefits, including high production rates, consistent dimensional accuracy, the ability to create complex geometries, material versatility, and cost-effective mass production.