- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.
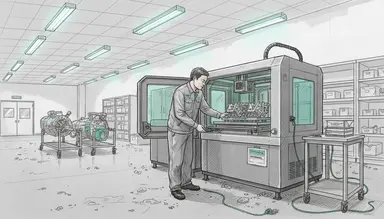
Complex component designs often push the boundaries of traditional manufacturing in China’s aerospace and automotive sectors. As rapid prototyping and low-volume production drive product development, many engineers are looking for ways to produce intricate metal parts efficiently. Metal 3D printing solutions offer enhanced design freedom, precision, and material efficiency, making them a valuable tool for advancing engineering projects and meeting challenging timelines.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Metal 3D Printing Enhances Design Flexibility | The layer-by-layer additive process allows for complex geometries and innovative designs that traditional methods cannot achieve. |
| Diverse Methods for Various Applications | Different metal 3D printing techniques provide unique advantages suited for aerospace, automotive, and medical industries. |
| Material Selection is Crucial | Choosing the appropriate metal material affects performance, cost, and production efficiency; thorough evaluation is essential. |
| Addressing Technical Challenges is Key | Implementing advanced monitoring and control techniques can overcome manufacturing challenges and improve reliability in metal 3D printing. |
Metal 3D printing represents a revolutionary manufacturing technology that enables engineers and designers to create complex metal components through an additive layer-by-layer fabrication process. Advanced metal additive manufacturing techniques have transformed traditional manufacturing workflows by offering unprecedented design flexibility and precision.
The core principle of metal 3D printing involves digitally guided material deposition, where specialized metal powders are selectively melted and fused to create three-dimensional objects directly from computer-aided design (CAD) models. This transformative process enables manufacturers to produce intricate geometries that would be impossible or extremely challenging with conventional subtractive manufacturing methods.
Key characteristics of metal 3D printing include:
Metal additive manufacturing technologies can be categorized into several primary methods, each with unique capabilities:
These processes differ in their specific mechanisms of depositing and fusing metal materials, offering engineers diverse options for creating precision components across aerospace, automotive, medical, and industrial sectors.
Pro tip: Always consult material and equipment specifications to determine the most suitable metal 3D printing technique for your specific engineering requirements.
Metal additive manufacturing technologies offer diverse approaches for creating complex metal components, each with unique capabilities and industrial applications. Common metal printing methods enable engineers to select optimal techniques based on specific design requirements and performance constraints.
The primary metal 3D printing methods can be categorized into four fundamental approaches, each representing a distinct technological strategy for material deposition and component fabrication:
Each method presents distinct advantages and limitations, making technology selection critical for achieving desired mechanical properties, surface finish, and geometric complexity. Powder Bed Fusion techniques, for instance, offer exceptional precision and fine detail reproduction, while Directed Energy Deposition methods excel in creating large-scale components with robust material deposition.
Industrial applications vary significantly across these technologies, with aerospace, automotive, medical device manufacturing, and precision engineering representing key sectors leveraging advanced metal 3D printing capabilities. The choice of method depends on factors including part complexity, material requirements, production volume, and economic considerations.
Here's a comparison of leading metal 3D printing methods and their best-fit industry applications:
| Method | Best Industry Use | Precision Level | Typical Part Size |
|---|---|---|---|
| Selective Laser Melting | Aerospace components | Very high | Small to medium |
| Binder Jetting | Automotive prototyping | Moderate | Medium to large |
| Directed Energy Depos. | Repair, heavy industry | Good | Large |
| Sheet Lamination | Low-cost tooling | Fair | Medium |
Pro tip: Consult with metallurgical experts and conduct thorough prototype testing to validate the most appropriate metal 3D printing method for your specific engineering application.
Metal 3D printing materials represent a critical foundation for achieving exceptional performance in precision engineering applications. Advanced metallic composite materials enable engineers to develop complex components with tailored mechanical properties and enhanced functional characteristics.
The most popular materials for precision metal 3D printing can be categorized into several key groups:
Each material category offers unique advantages for specific industrial applications. Stainless steel variants provide excellent corrosion resistance and mechanical strength, making them ideal for medical and automotive components. Aerospace-grade metals like titanium alloys deliver exceptional strength-to-weight ratios critical for aerospace and advanced engineering sectors.
Manufacturing considerations such as thermal conductivity, melting point, powder characteristics, and post-processing requirements significantly influence material selection. Engineers must carefully evaluate mechanical properties, surface finish potential, and economic factors when choosing metal 3D printing materials for precision parts.
For quick reference, here's a summary of major metal 3D printing material categories and their benefits:
| Material Category | Primary Advantage | Common Industries |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High strength, corrosion resistance | Medical, automotive |
| Titanium Alloys | Lightweight, biocompatible | Aerospace, medical |
| Nickel Superalloys | Heat tolerance, durability | Aerospace, energy |
| Copper Alloys | High conductivity | Electronics, tooling |
| Cobalt-Chrome | Wear resistance, bioimplants | Medical devices |
Pro tip: Conduct comprehensive material testing and collaborate with metallurgical experts to validate the most suitable metal alloy for your specific engineering requirements.
Metal 3D printing technologies have revolutionized manufacturing capabilities in aerospace and automotive industries, enabling unprecedented design flexibility and performance optimization. Advanced additive manufacturing techniques are transforming how critical components are designed, produced, and integrated into complex mechanical systems.
Key application areas in these industries include:
Aerospace Applications:
Automotive Applications:
The transformative potential of metal 3D printing lies in its ability to produce geometrically complex parts with exceptional material efficiency. Aerospace engineers can now create turbine blades with intricate cooling channels that were previously impossible with traditional manufacturing methods. Similarly, automotive manufacturers can develop lightweight components that significantly reduce vehicle weight and improve overall performance.

These advanced manufacturing techniques offer substantial advantages, including reduced material waste, faster production cycles, and the ability to create parts with optimized internal structures that enhance mechanical properties. The technology enables engineers to move beyond traditional design constraints, exploring innovative solutions that were once considered technically unfeasible.
Pro tip: Collaborate closely with metallurgical experts and leverage computational modeling to maximize the potential of metal 3D printing in your engineering design process.
Metal 3D printing economics represent a complex interplay of technological capabilities and financial considerations. Strategic cost management approaches are critical for manufacturers seeking to optimize their additive manufacturing workflows and maintain competitive advantage.
Key cost factors in metal 3D printing include:
Material Expenses:
Equipment and Processing Costs:
Quality Control Considerations:
The relationship between cost, quality, and speed is intricate and interdependent. Higher-quality metal powders typically increase production expenses but can significantly improve final component performance. Manufacturers must carefully balance material selection, machine utilization, and post-processing requirements to achieve optimal economic outcomes.
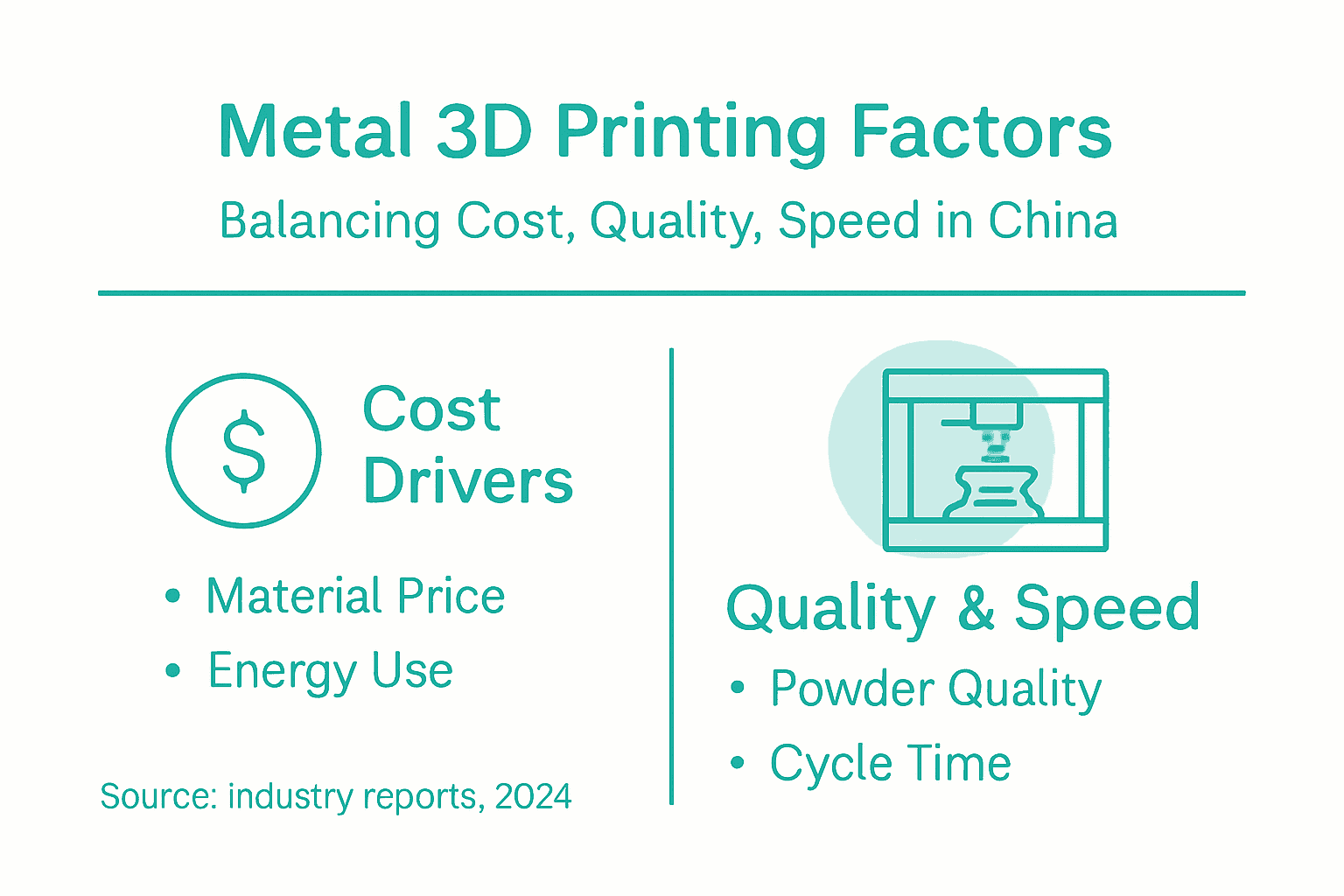
Advanced software and sophisticated process parameters can help mitigate production inefficiencies, reducing lead times and minimizing material waste. Implementing risk-based inspection strategies and leveraging computational modeling techniques enables engineers to predict and control manufacturing variability more effectively.
Pro tip: Develop comprehensive cost-modeling strategies that integrate material, equipment, and quality control expenses to accurately predict and optimize metal 3D printing production economics.
Metal 3D printing technologies continue to evolve, presenting complex engineering challenges that require sophisticated solutions. Advanced error detection and process optimization strategies are critical for manufacturers seeking to improve reliability and performance in additive manufacturing workflows.
Key challenges in metal 3D printing include:
Design and Preprocessing Challenges:
Technical Performance Barriers:
Process Control Best Practices:
Successful metal 3D printing requires a holistic approach that addresses technical, material, and process-related challenges. Engineers must develop comprehensive strategies that integrate design optimization, precise material selection, and advanced process control techniques to mitigate potential manufacturing variabilities.
Industry experts recommend continuous innovation in equipment, materials, and process parameters to overcome current technological limitations. Scaling production, automating complex workflows, and investing in emerging technologies like binder jetting can help manufacturers reduce costs and expand the practical applications of metal additive manufacturing.
Pro tip: Implement comprehensive process monitoring and develop rigorous quality control protocols to systematically identify and mitigate potential manufacturing defects in metal 3D printing.
Facing challenges like material selection, balancing cost, quality, and speed, or overcoming technical barriers such as porosity control and residual stress management? This article highlights these critical pain points and the need for expert guidance in adopting advanced metal additive manufacturing technologies. Whether you require precision aerospace-grade components or automotive prototypes with complex geometries, mastering methods like DMLS or Binder Jetting is essential for maximizing design freedom and performance.
At WJ Prototypes, we specialize in delivering high-quality, cost-effective metal 3D printing solutions tailored to your unique project demands. Our experienced engineers leverage cutting-edge processes including Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS) combined with comprehensive materials expertise to ensure your parts meet rigorous standards with rapid turnaround. Discover how our integrated prototyping and low-volume manufacturing services empower you to innovate confidently and accelerate time to market.
Take the next step to elevate your product development experience by partnering with WJ Prototypes. Explore our full range of advanced manufacturing services and get an instant quote to start transforming your metal 3D printing challenges into competitive advantages today.
Metal 3D printing technology is an additive manufacturing process that creates complex metal components layer by layer using specialized metal powders, which are melted and fused according to digital designs.
The primary methods of metal 3D printing include Selective Laser Melting (SLM), Direct Metal Laser Sintering (DMLS), Electron Beam Melting (EBM), Binder Jetting, and Directed Energy Deposition (DED).
Metal 3D printing offers numerous advantages, including the ability to create intricate geometries, reduced material waste, enhanced design freedom, and the capability to manufacture complex internal structures that would be challenging with conventional methods.
Common materials for metal 3D printing include stainless steel alloys, aerospace-grade metals like titanium and aluminum, and high-performance specialty metals such as nickel superalloys and cobalt-chrome alloys.
Trends And Future Of 3D Printing Services in China
What Is Industrial 3D Printing? Complete Guide by WJ Prototypes
Global B2B Demand for 3D Printed Parts - WJ Prototype
On-Demand 3D Printing Services for Your Business Needs
Branchenvorteile Lasertechnik: Effizienzsteigerung Und Innovationen