- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.


Complex product challenges in fields like Aerospace and Medical Device engineering often demand solutions that adapt quickly and minimise costly delays. Iterative prototyping empowers design teams to advance their concepts with each cycle, drawing on fresh feedback and systematically increasing model sophistication. By focusing on continuous learning and incremental improvements, this approach offers a practical pathway to smarter, faster development. Understand how iterative prototyping cycles generate knowledge across every stage of product creation, supporting better decisions and superior outcomes.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Iterative Prototyping | This methodology allows for continual refinement of product designs through successive prototype versions, reducing risks and enhancing user requirements alignment. |
| Feedback Integration | Systematic incorporation of feedback from various stakeholders is crucial for refining prototypes and ensuring user-centric designs. |
| Cost, Speed, Quality Benefits | Iterative prototyping enhances efficiency by identifying design issues early, lowering costs, accelerating time to market, and improving product quality. |
| Common Pitfalls | Insufficient stakeholder engagement and poor documentation can undermine the effectiveness of iterative approaches, leading to wasted resources and lost insights. |
Iterative prototyping represents a dynamic approach to product design that enables continuous refinement and improvement through successive model developments. At its core, this methodology involves creating multiple versions of a prototype, each building upon previous insights and learnings. Prototyping methods systematically generate knowledge throughout product development phases, supporting critical design decision-making processes.
The fundamental concept of iterative prototyping involves exploring both problem and solution domains by creating early product models that simulate potential design outcomes. These prototypes range from basic sketches to increasingly sophisticated representations, enabling designers to validate and improve designs incrementally. By continuously refining prototypes across multiple stages, teams can reduce risks, validate user requirements, and develop more robust product solutions.
Key characteristics of iterative prototyping include its cyclical nature, emphasis on learning, and progressive complexity. Designers start with simple, low-fidelity representations and progressively develop more detailed and sophisticated models. Each iteration involves gathering feedback, analysing performance, and making targeted improvements. This approach allows teams to identify and address potential design challenges early in the development process, ultimately reducing overall development time and minimising expensive late-stage modifications.
Pro Tip: When implementing iterative prototyping, maintain meticulous documentation of each prototype version to track design evolution and capture critical insights throughout the development cycle.
Prototyping methods encompass a diverse range of approaches that allow designers to explore and validate product concepts through various representational strategies. Prototyping techniques span from low to high-fidelity models, enabling teams to progressively develop and refine design solutions across different stages of product development.

Two primary prototyping approaches dominate product design methodologies: parallel and iterative prototyping. Parallel prototyping involves simultaneously exploring multiple design concepts, allowing teams to compare and contrast different solutions concurrently. This method is particularly effective when designers want to generate diverse ideas and evaluate multiple potential directions. In contrast, iterative prototyping focuses on progressively refining a single design concept through repeated cycles of development, feedback, and improvement.
The selection of a prototyping method depends on several critical factors, including project complexity, available resources, timeline, and specific design objectives. Low-fidelity prototypes such as paper sketches and basic wireframes are ideal for initial concept exploration, while high-fidelity interactive mockups and functional prototypes provide more detailed insights into potential product performance. Each prototyping method offers unique advantages, enabling designers to balance creativity, technical feasibility, and user requirements throughout the product development process.
Here is a comparison of parallel and iterative prototyping approaches:
| Aspect | Parallel Prototyping | Iterative Prototyping |
|---|---|---|
| Main Focus | Exploring multiple concepts | Refining one concept repeatedly |
| Ideal Stage | Early ideation and concept selection | Ongoing development and validation |
| Team Involvement | Broader engagement, diverse inputs | Focused, detailed improvement cycles |
| Risk Mitigation | Reduces bias through variety | Mitigates errors via gradual refinement |
| Outcome | Wide range of alternatives | Highly polished final product |
Pro Tip: Choose your prototyping method strategically by considering your project's specific constraints and objectives, and be prepared to adapt your approach as design insights emerge.
Feedback integration is the cornerstone of effective iterative prototyping, transforming design processes by systematically incorporating insights from multiple stakeholders. Prototyping cycles enable continuous user input, allowing design teams to progressively refine product concepts based on real-world observations and expert perspectives.
The feedback integration process typically involves structured evaluation stages where each prototype version undergoes rigorous assessment. Stakeholders including end-users, engineers, marketers, and potential customers provide critical perspectives that highlight potential improvements, usability challenges, and design opportunities. By collecting diverse viewpoints, designers can identify subtle nuances and potential issues that might not be apparent during initial concept development, ensuring a more comprehensive and user-centric design approach.
Technically, feedback integration occurs through multiple channels such as user testing sessions, interviews, surveys, and performance analysis. Each feedback cycle generates quantitative and qualitative data that directly informs subsequent prototype iterations. Design teams analyse these inputs systematically, prioritising changes that address critical user needs, technical feasibility, and overall product performance. This methodical approach transforms initial conceptual designs into progressively more refined and market-aligned solutions, minimising development risks and maximising product potential.
Pro Tip: Document all feedback comprehensively, categorising insights by source, impact, and implementation complexity to streamline your iterative design process.
Aerospace and medical sectors leverage iterative prototyping as a critical methodology for developing complex, high-stakes technologies that demand exceptional precision and reliability. These industries rely on systematic design refinement to address intricate engineering challenges, regulatory requirements, and stringent performance standards.
In aerospace engineering, iterative prototyping plays a pivotal role in developing advanced components and systems. Engineers utilise multiple prototype iterations to validate aerodynamic designs, test structural integrity, and optimise complex mechanical interfaces. Critical systems such as aircraft control mechanisms, propulsion components, and lightweight structural elements undergo rigorous testing and refinement, ensuring maximum safety and performance before final production.
The medical device sector similarly demonstrates remarkable application of iterative prototyping techniques. Medical engineers and designers use successive prototype generations to develop intricate devices that must meet extraordinary functional and safety requirements. From surgical instruments to implantable medical technologies, each prototype represents an opportunity to enhance usability, improve patient outcomes, and address complex biomechanical challenges. These iterative processes enable designers to integrate cutting-edge materials, advanced manufacturing techniques, and precise engineering solutions that directly impact human health and medical interventions.
Pro Tip: Maintain comprehensive documentation of each prototype iteration, tracking specific modifications, performance metrics, and design rationales to support continuous improvement and regulatory compliance.
Iterative prototyping delivers significant advantages in balancing development costs, time efficiency, and product quality. By enabling rapid design exploration and continuous refinement, this approach transforms traditional product development methodologies, allowing organisations to optimise resource allocation and minimise expensive late-stage modifications.
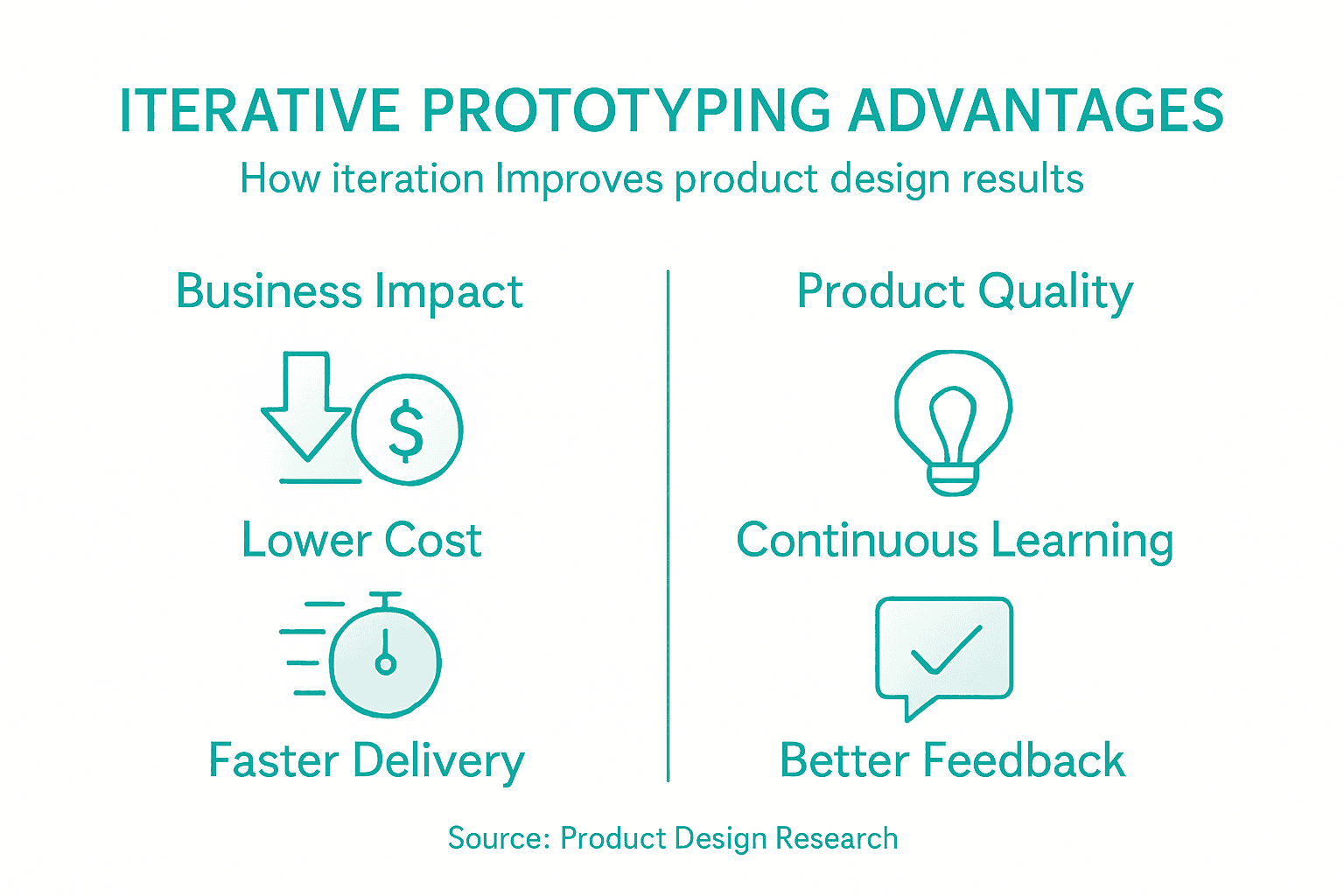
The speed advantage of iterative prototyping stems from its ability to identify and resolve design challenges early in the development cycle. Traditional linear design approaches often result in lengthy development periods and substantial financial investments before critical issues are discovered. In contrast, iterative prototyping allows teams to test multiple design concepts quickly, gather immediate feedback, and make targeted improvements without committing extensive resources to a single approach.
Quality improvements represent another substantial benefit of iterative prototyping. Each prototype iteration generates valuable insights that incrementally enhance product functionality, usability, and performance. By continuously validating design assumptions against real-world requirements, engineers can systematically eliminate potential weaknesses, reduce technical risks, and develop more robust solutions. This approach ensures that final products not only meet but frequently exceed initial design specifications, delivering superior value to end-users and stakeholders.
Below is a summary of key advantages delivered by iterative prototyping:
| Advantage | Description | Business Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Efficiency | Early issue detection reduces redesign costs | Saves budget on late corrections |
| Speed | Rapid feedback accelerates decisions | Shorter time to market |
| Quality | Continuous testing improves robustness | Enhanced user satisfaction |
| Knowledge Gain | Learning at each stage builds expertise | Stronger innovation capability |
Pro Tip: Establish clear metrics and feedback mechanisms for each prototype iteration to objectively measure improvements and maintain a structured approach to design refinement.
Iterative prototyping mistakes can significantly derail product development by undermining the core principles of continuous improvement and systematic design refinement. Understanding these common pitfalls is crucial for teams seeking to maximise the effectiveness of their prototyping strategies and avoid costly design errors.
One prevalent mistake involves insufficient stakeholder engagement and poorly defined iteration objectives. Design teams often fall into the trap of creating prototypes without clear evaluation criteria, leading to unfocused iterations that consume resources without generating meaningful insights. This lack of strategic direction results in prototypes that fail to address critical design challenges or provide actionable feedback, effectively nullifying the potential benefits of the iterative approach.
Another significant error is the inconsistent documentation and knowledge management throughout the prototyping process. Each prototype iteration generates valuable learnings, but many teams neglect systematic recording of design decisions, performance observations, and stakeholder feedback. Without a robust documentation strategy, organisations lose critical institutional knowledge, making it difficult to track design evolution, understand previous design choices, and build upon accumulated insights from earlier prototype generations.
Pro Tip: Establish a standardised documentation template for each prototype iteration, capturing key design parameters, performance metrics, and feedback insights to create a comprehensive knowledge repository.
Iterative prototyping is essential for refining design concepts through repeated improvements and careful integration of feedback. If you recognise the challenges of managing multiple prototype versions, maintaining quality, and reducing costly late-stage changes, you need a partner who can bring precision engineering and rapid turnaround to your project. At WJ Prototypes, we specialise in supporting iterative processes with advanced manufacturing technologies including SLA, SLS, CNC machining, and vacuum casting. Our expertise across aerospace, medical, and industrial sectors ensures your prototypes evolve efficiently from concept to finalised design with meticulous documentation and quality assurance.
Discover how our comprehensive prototyping solutions can address your need for speed, cost control, and high-quality outcomes throughout your product development cycle. Take the next step and explore our capabilities at WJ Prototypes to leverage a trusted manufacturing partner. Request an instant quote today and transform your iterative prototyping challenges into successes with our rapid prototyping services. Your innovative ideas deserve expert execution now.
Iterative prototyping is a methodology that involves creating multiple versions of a prototype, refining and improving it through successive developments to enhance product design based on user feedback and insights.
Iterative prototyping streamlines the development process by allowing for early detection of issues, reducing risks, and ensuring that user requirements are met through continuous refinement and testing of prototype iterations.
Common methods include low-fidelity prototypes like sketches and wireframes for initial concepts, as well as high-fidelity models such as interactive mockups that provide detailed insights into product performance.
Feedback integration is crucial as it enables design teams to gather perspectives from stakeholders, helping them to identify usability challenges and inform improvements, ultimately leading to a more user-centric and market-aligned product.
A Comprehensive Guide To Prototyping in Product Design
Role of Prototyping in Product Development: Complete Guide
What Is The Role of Engineers in Prototyping – Driving Innovation
Rapid Prototyping Guide | 5 Important Steps To Prototype Design & Manufacturing
Laser im Prototyping: Präzision und Effizienz im Fokus