- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.


Every CNC machinist knows that preparing equipment and choosing the right cutting tools sets the tone for the entire manufacturing process. In the high-stakes world of aerospace and automotive machining, even the smallest oversight can compromise both precision and speed. This detailed guide walks you through every stage, starting with meticulous machine preparation and strategic tool selection, so you can achieve superior results and keep production on schedule.
| Key Point | Explanation |
|---|---|
| 1. Thoroughly prepare your CNC machine | Inspect, clean, and calibrate the machine to ensure it operates smoothly and accurately for machining tasks. |
| 2. Choose the right cutting tools | Select tools based on material properties, considering factors such as hardness and cutting speed for optimal performance. |
| 3. Secure workpieces properly | Use appropriate workholding devices and ensure secure mounting to prevent movement during the machining process, which ensures precision. |
| 4. Input and verify machining programs meticulously | Carefully enter and check the CNC program against the design specs, using simulation software to avoid errors before execution. |
| 5. Implement rigorous quality inspections | Systematically measure and validate components using calibrated tools to ensure they meet design specifications and quality standards. |
Successful CNC machining requires meticulous preparation and strategic tool selection. In this stage, you will set up your machine and choose the optimal cutting tools to ensure precision manufacturing results.
Beginning with machine preparation, carefully inspect your CNC equipment for any signs of wear or misalignment. Computer numerical control fundamentals emphasise the importance of a clean, calibrated workspace. Start by thoroughly cleaning the machine bed, removing any debris or metal shavings from previous operations. Check all axis movements to confirm smooth, unobstructed motion. Verify that your coordinate systems are correctly configured and that the machine's referencing points align precisely.
Tool selection is a critical aspect of CNC machining that directly impacts your manufacturing quality. Evaluate the specific material you are working with and choose tools designed for optimal performance. High-speed steel, carbide, and ceramic tools each have unique properties suited to different applications. Consider factors such as cutting speed, feed rate, and material hardness when selecting your cutting implements. Ensure your tool holders are compatible with the selected tools and securely fastened to prevent vibration or potential safety risks.
Here is a quick comparison of common CNC cutting tool materials and their ideal applications:
| Tool Material | Key Properties | Suitable Applications |
|---|---|---|
| High-speed steel | Durable, easy to sharpen | General purpose machining |
| Carbide | Maintains hardness at high temps | High precision, hard materials |
| Ceramic | Extremely heat resistant | High speed, non-ferrous alloys |
Expert Recommendation: Always maintain a comprehensive inventory of calibrated tools and perform regular tool inspections to prevent unexpected machining interruptions.
Successful CNC machining relies on precise material preparation and robust workpiece securing techniques. In this critical stage, you will learn how to position and stabilise your materials to ensure accurate and consistent manufacturing results.
Workholding principles are fundamental to achieving high-precision machining outcomes. Begin by selecting appropriate workholding devices such as precision vises, clamps, or custom fixtures that match your specific material and part geometry. Carefully clean the mounting surface to remove any debris or contaminants that could compromise alignment. When positioning your workpiece, ensure it is mounted squarely and symmetrically within the machine's working envelope. Pay close attention to referencing surfaces and datum points that will guide subsequent machining operations.
Material preparation involves more than just physical mounting. Evaluate the material's mechanical properties and potential for deformation during machining. For softer materials like aluminium, use graduated clamping pressures to prevent distortion. For harder materials such as stainless steel, select robust workholding solutions that provide maximum rigidity. Always leave sufficient exposed surface area for tooling access while maintaining secure contact points that distribute clamping force evenly across the workpiece.

Expert Recommendation: Create a standardised workholding checklist for each material type to ensure consistent setup and reduce potential errors in your machining process.
Precision CNC machining demands meticulous programme input and comprehensive verification to ensure accurate manufacturing outcomes. This critical stage transforms your design blueprints into executable machine instructions that will guide the entire manufacturing process.
Computer numerical control programming requires careful attention to detail and systematic verification. Begin by carefully translating your technical drawings into precise G-code commands, ensuring each coordinate, tool movement, and machining parameter is accurately represented. Review the programme line by line, checking for potential conflicts or unexpected movements that could compromise part quality or machine safety. Pay close attention to coordinate systems, tool offset calculations, and feed rate specifications. Utilise simulation software to preview the entire machining sequence before actual execution, allowing you to identify and rectify any potential programming errors.
Verification involves more than just programme review. Cross reference your CNC programme with the original design specifications, checking dimensional tolerances, tool paths, and machining sequences. Confirm that each tool change, spindle speed, and cutting strategy matches the intended manufacturing approach. For complex parts, consider running a test programme on a sacrificial workpiece to validate the programme's accuracy and identify any subtle programming nuances that might not be immediately apparent during digital simulation.
Expert Recommendation: Create a comprehensive programme verification checklist that includes dimensional checks, tool path validation, and safety protocol confirmations to minimise potential machining errors.
CNC machining execution represents the culmination of careful preparation and precision planning. This critical stage transforms your meticulously prepared programme and workpiece into a finished manufactured component through controlled, systematic mechanical operations.
Machining process automation requires systematic monitoring and continuous adjustment throughout the manufacturing cycle. Initiate the machining sequence by confirming all safety protocols and verifying that the machine parameters match your programmed specifications. Carefully observe the initial cutting passes, paying close attention to tool engagement, material response, and potential vibration or unexpected resistance. Monitor spindle speed, feed rates, and cutting conditions in real time, prepared to make incremental adjustments that maintain optimal machining performance.
As the machining operation progresses, remain vigilant about potential process variations. Implement periodic dimensional checks to ensure the emerging part matches design specifications precisely. Use measuring instruments such as micrometres and vernier callipers to validate critical tolerances at predetermined intervals. For complex geometries, consider breaking the machining process into multiple stages, allowing for intermediate inspections and potential programme refinements. This methodical approach minimises the risk of catastrophic errors and supports consistent, high quality manufacturing outcomes.
Expert Recommendation: Develop a standardised operational checklist that includes real time monitoring points, measurement verification stages, and contingency protocols to maintain manufacturing precision.
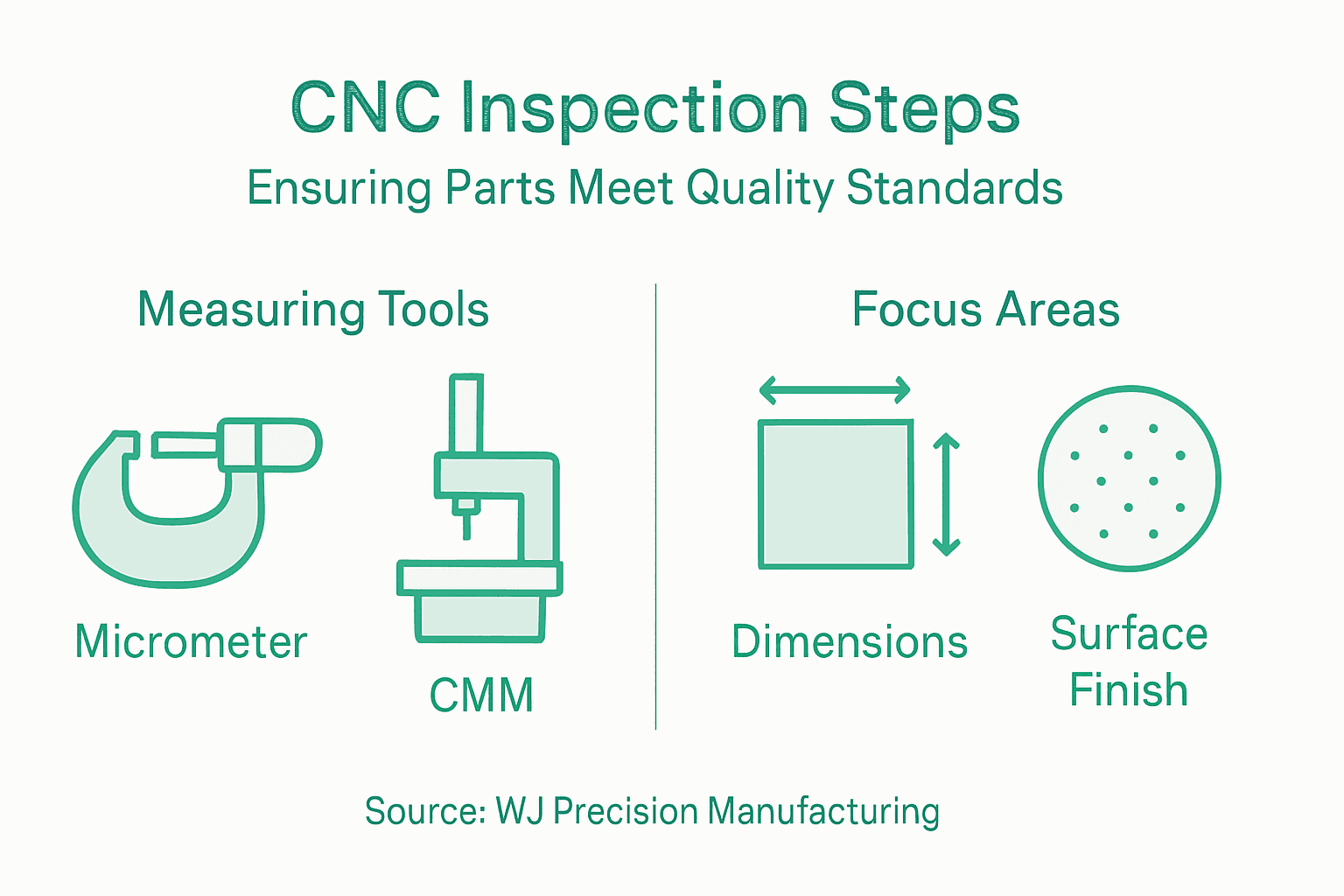
Component inspection represents the final critical checkpoint in precision manufacturing where theoretical design meets actual production performance. Your objective is to systematically validate every manufactured part against original engineering specifications and quality benchmarks.
Quality inspection techniques require a comprehensive and methodical approach. Begin by selecting appropriate measuring instruments calibrated to detect minute variations. Employ precision tools such as micrometres, coordinate measuring machines (CMM), digital callipers, and optical comparators to assess dimensional accuracy. Conduct thorough visual and tactile inspections, checking surface finish, geometric tolerances, and material consistency. Systematically measure critical dimensions against the original part print, recording measurements in a standardised documentation system that allows traceability and future reference.
This table summarises essential inspection instruments used in CNC component quality assurance:
| Instrument | Primary Use | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Micrometre | Measuring diameter/thickness | Small precise dimensions |
| Coordinate measuring machine (CMM) | 3D dimensional measurement | Complex part geometries |
| Digital calliper | Quick length and width checks | General measurement tasks |
| Optical comparator | Visual profile and angle analysis | Fine detail and angles |
Quality assurance extends beyond dimensional verification. Evaluate the part's mechanical properties, surface integrity, and functional performance potential. Perform hardness tests, assess material grain structure, and check for potential micro-fractures or stress concentrations that might compromise component reliability. Where applicable, conduct non destructive testing methods like ultrasonic or magnetic particle inspections to identify hidden material defects. Create a comprehensive inspection report documenting every measurement, deviation, and quality assessment to maintain transparent manufacturing records.
Expert Recommendation: Develop a rigorous inspection protocol with statistically validated measurement techniques that allow for consistent and reproducible quality assessment across all manufactured components.
The journey to CNC machining success starts with meticulous preparation, precise tool selection, and thorough programme verification. Challenges such as ensuring workpiece stability, monitoring cutting conditions, and rigorous quality inspection can slow down your manufacturing process or compromise part accuracy. This article highlights critical phases like aligning coordinate systems, selecting appropriate cutting tools, and validating programmes, all vital for delivering parts that meet exacting specifications.
If maintaining consistent manufacturing precision while saving time and costs sounds essential to you discover how WJ Prototypes can be your trusted partner. Our professional CNC machining services combine advanced equipment with expert engineering support to help you avoid common pitfalls in tool wear, setup errors, and inspection inconsistencies. Benefit from our comprehensive range of services including rapid prototyping and small to medium production runs designed for industries demanding high precision such as aerospace and medical sectors.
Explore the advantages of working with a reliable manufacturer who understands the intricacies of CNC machining and can provide tailored solutions that guarantee quality and speed. Take the next step toward seamless production by contacting WJ Prototypes today and request your instant quote to bring your precision manufacturing projects to life with confidence.
Successful CNC machining begins with meticulous machine preparation and tool selection. Begin by inspecting your CNC equipment for wear and misalignment, and ensure you have chosen the correct tools based on the material you’ll be machining.
To secure your workpieces, choose appropriate workholding devices such as precision vises or custom fixtures. Clean the mounting surfaces thoroughly and ensure the workpiece is mounted squarely to prevent any movement during machining.
The machining programme verification process should include checking all G-code commands for accuracy and ensuring that tool movements match the original design specifications. Review the programme line by line and run a test programme on a sacrificial workpiece to confirm accuracy before executing it on the final material.
To monitor CNC machining effectively, observe initial cutting passes for tool engagement and material response. Implement periodic dimensional checks using measuring instruments to ensure that the manufactured part meets the design specifications throughout the machining process.
Key instruments for inspecting CNC components include micrometres, coordinate measuring machines (CMM), and digital callipers. Use these tools to assess dimensional accuracy and document measurements in a standardised format for traceability.
Developing a rigorous inspection protocol involves establishing statistically validated measurement techniques for consistent quality assessment. Create a checklist that includes dimensional checks, surface quality evaluations, and potential non-destructive testing methods to ensure reliable manufacturing outcomes.
Complete Guide to the Role of CNC Machining - WJ Prototypes
CNC Machining Instructions | Step-by-Step Guide to Sourcing from China
Precision CNC Machining in China | Fast, Flexible & Reliable Manufacturing
Precision Machining in China | Why China Leads Global Production
CNC-Lasern erklärt: Verfahren, Anwendungen, Vorteile