- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.


Over 90% of successful medical device launches begin with a robust prototyping phase. For anyone involved in healthcare innovation, understanding this early process often makes the difference between breakthrough and setback. This overview sheds light on how global engineers combine creative design with methodical prototyping so you can grasp the essential steps, avoid common pitfalls, and discover which strategies deliver safe, effective results.
Prototyping plays a vital role in medical device development by ensuring safety, performance, and regulatory readiness before full-scale production. Through rapid prototyping, manufacturers can validate designs, test materials, and identify potential risks early in the development cycle. China has become a preferred destination for medical device prototyping due to its advanced manufacturing capabilities, fast turnaround times, and cost efficiency. By combining precision machining, strict quality control, and rapid iteration, Chinese prototyping partners help medical device companies accelerate innovation while meeting stringent safety and compliance requirements.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Importance of Prototyping | Prototyping is essential for transforming medical device concepts into functional models, allowing for early testing and refinement. |
| Types of Prototypes | Medical device prototypes range from conceptual to functional, each serving a distinct purpose in the development process. |
| Regulatory Compliance | Navigating regulatory requirements is crucial, necessitating thorough documentation and testing to ensure safety and effectiveness. |
| Challenges in Prototyping | Strategic planning is vital to manage costs, material selection, and design complexities effectively during prototyping. |
Medical device prototyping is a critical engineering process that transforms conceptual designs into tangible, functional representations enabling researchers and manufacturers to test, validate, and refine potential medical technologies. Early-stage prototyping fundamentally involves exploring device form and function using versatile materials like foam core, off-the-shelf components, and advanced 3D printing techniques.
The primary objective of medical device prototyping is to create initial models that simulate actual product performance, allowing engineers to assess critical parameters such as ergonomics, mechanical functionality, and potential user interactions. By constructing preliminary versions, design teams can systematically evaluate technical feasibility, identify potential manufacturing challenges, and iteratively improve device concepts before committing to full-scale production. These prototype models serve as crucial communication tools, helping stakeholders visualise complex medical technologies and validate design assumptions.
Medical device prototyping encompasses several sophisticated methodological approaches, including:
Through meticulous prototyping strategies, medical device manufacturers can significantly reduce development risks, optimise design efficiency, and ultimately deliver safer, more innovative healthcare technologies.
Medical device prototypes represent a sophisticated spectrum of design representations, ranging from preliminary conceptual models to highly advanced functional demonstrations. Medical device prototypes can span from simple whiteboard sketches to complex precision-machined components, each serving a distinct purpose in the product development lifecycle.
Typically, medical device prototypes are categorised into two primary classifications: form models and function models. Form models explore the device's shape, ergonomics, and physical characteristics, while function models focus on testing technical feasibility, mechanical interactions, and electronic integrations. These prototypes enable engineers to validate design concepts, assess user interactions, and identify potential manufacturing challenges before committing to final production.
The primary types of medical device prototypes include:
Engineers typically progress through these prototype stages systematically, refining design complexity and technical sophistication with each iteration. This methodical approach allows medical device manufacturers to mitigate development risks, optimise product performance, and ensure stringent quality standards are consistently met.
Medical device prototyping is a systematic engineering approach that transforms innovative concepts into functional healthcare solutions. The prototyping process begins with initial concept development, exploring device shape and ergonomics through form models, ultimately progressing towards sophisticated functional representations.

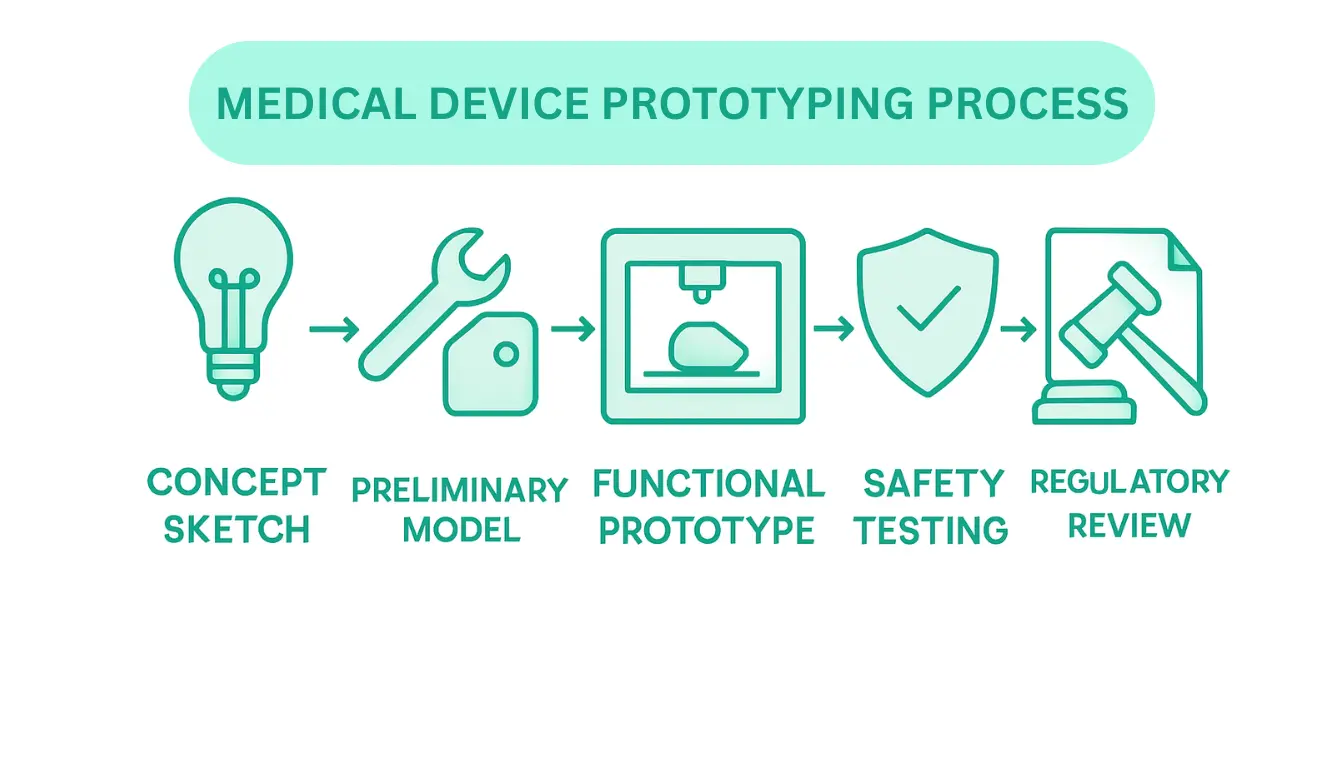
The comprehensive prototyping process typically encompasses five interconnected stages, each designed to incrementally refine and validate medical device design. These stages require meticulous attention to technical details, user requirements, and regulatory compliance. Engineers must carefully navigate each phase, understanding that every iteration brings the concept closer to a viable medical technology.
The key stages of medical device prototyping include:
Successful medical device prototyping demands a disciplined, systematic approach that balances innovative design with stringent safety and performance requirements. By methodically progressing through these stages, engineers can transform conceptual ideas into life-changing medical technologies that meet the highest standards of healthcare innovation.
Medical device prototyping involves navigating a complex landscape of regulatory requirements that ensure patient safety and product effectiveness. Prototyping must systematically address rigorous testing criteria to demonstrate safety, effectiveness, and compliance with established medical standards, making regulatory considerations an integral aspect of the design process.
The regulatory framework for medical device prototyping encompasses multiple critical dimensions, including stringent documentation, comprehensive performance testing, and adherence to international quality standards. Manufacturers must meticulously document each prototype iteration, capturing detailed design modifications, performance characteristics, and risk assessments. This documentation serves as evidence of the device's developmental progression and provides a transparent trail for regulatory bodies to review and validate.
Key regulatory compliance factors include:
Successful medical device prototyping demands a proactive approach to regulatory compliance, where engineers must anticipate and address potential regulatory challenges throughout the development process. By integrating compliance considerations from the earliest design stages, manufacturers can streamline their path to market approval while maintaining the highest standards of patient safety and product quality.
Medical device prototyping demands strategic financial and technical planning, with numerous potential challenges that can significantly impact project budgets and timelines. Designers must carefully balance cost considerations with quality requirements, navigating complex material selection and iterative design processes, understanding that each design modification carries substantial economic implications.
The primary cost implications in medical device prototyping emerge from multiple interconnected factors, including material expenses, technological complexity, testing requirements, and regulatory compliance. Engineers must anticipate potential financial risks by implementing robust design strategies that minimise unnecessary iterations while maintaining high-performance standards. Unexpected design challenges can exponentially increase development costs, making proactive risk management crucial for successful project execution.
Key potential pitfalls in medical device prototyping include:
Successful medical device prototyping requires a sophisticated approach that anticipates potential financial and technical challenges. Engineers must develop comprehensive strategies that balance innovative design, rigorous testing, and cost-effective development processes, ultimately delivering high-quality medical technologies that meet stringent performance and regulatory standards.
Medical device prototyping encompasses a diverse range of technologies and methodological approaches, each offering unique advantages in design, development, and testing. Prototyping methods utilise a spectrum of techniques ranging from off-the-shelf components to advanced microcontroller integration and sophisticated 3D printing technologies, enabling engineers to select the most appropriate strategy for specific design requirements.
The comparative landscape of prototyping technologies reveals nuanced trade-offs between speed, precision, cost-effectiveness, and functional complexity. Different methodologies excel in specific domains, with technologies like 3D printing offering rapid conceptual validation, while precision CNC machining provides exceptional dimensional accuracy for complex medical device components. Engineers must carefully evaluate multiple factors, including material compatibility, production scalability, and regulatory compliance when selecting appropriate prototyping approaches.
Key prototyping technologies and their distinctive characteristics include:
Successful medical device development requires a strategic approach to prototyping technology selection, balancing technical feasibility, economic constraints, and design complexity. By understanding the strengths and limitations of each prototyping method, engineers can develop innovative medical technologies that meet rigorous performance and safety standards.
When ensuring safety and speed in medical device development, overcoming challenges such as precise functional prototyping, rigorous regulatory compliance, and controlling costs is critical. The article highlights key pain points including designing ergonomic and functional models, iterative testing and refinement, and navigating complex regulatory landscapes. Achieving these goals requires access to advanced manufacturing technologies and expert engineering support to transform concepts into compliant, high-quality prototypes swiftly and cost-effectively.
WJ Prototypes specialises in delivering these exact capabilities through a comprehensive range of services including SLA, SLS, DMLS, CNC machining, vacuum casting, and injection moulding. Their expertise ensures precision engineering tailored for medical device prototyping challenges such as functional validation and regulatory compliance documentation. By leveraging WJ Prototypes’ ISO certified manufacturing and rapid turnaround times, designers can confidently move from conceptual design to production-ready models while controlling costs and minimising risks. Discover how WJ Prototypes can support your project’s success by exploring their advanced prototyping services and start accelerating your device development today. Visit WJ Prototypes and experience a partner dedicated to bringing innovative medical technologies to market faster.
Medical device prototyping is the engineering process that transforms conceptual designs into tangible, functional models, enabling testing, validation, and refinement of medical technologies.
The prototyping process typically involves five stages: conceptual design, preliminary prototype development, functional prototype creation, iterative testing and refinement, and validation and compliance.
Prototyping ensures safety by allowing comprehensive testing of each prototype against medical standards, documenting risk assessments, and validating compliance with regulatory requirements throughout the design process.
Common pitfalls include challenges in material selection, design complexity risks, regulatory compliance expenses, technical performance limitations, and economic miscalculations that can impact project budgets and timelines.