- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.
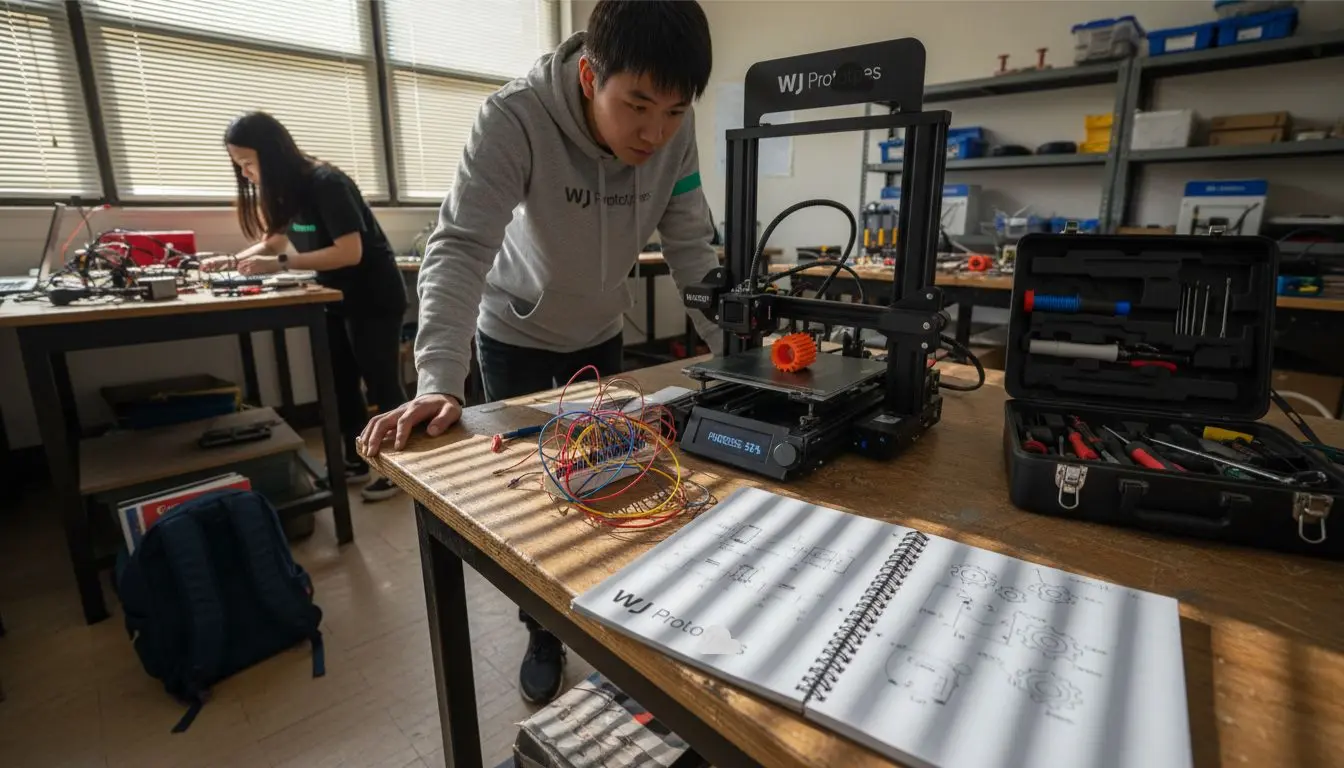

More than 80% of global manufacturers now rely on rapid prototyping to accelerate innovation and reduce costs. The demand for quicker product development cycles has grown as businesses face stiff competition in advanced sectors. Whether you are navigating the shifting world of design or aiming to produce the next breakthrough, understanding rapid prototyping can help you move from digital ideas to real-world testing with unmatched speed and precision.
Rapid prototyping has become a key advantage for precision manufacturing, allowing companies to validate designs, test functionality, and refine components with speed and accuracy. In China, rapid prototyping combines advanced CNC machining, 3D printing, and skilled engineering support to deliver highly precise parts at competitive costs. Short lead times and efficient supply chains enable faster design iterations, reduced development risks, and smoother transition from prototype to production. As a result, manufacturers worldwide leverage rapid prototyping in China to improve product quality, accelerate time to market, and maintain tight tolerances without compromising efficiency.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rapid Prototyping Revolutionises Manufacturing | Engineers can quickly create physical models from digital designs, significantly speeding up product development. |
| Additive vs Traditional Methods | Additive manufacturing excels in creating complex geometries, while traditional methods offer superior surface finishes. |
| Accelerated Innovation | Rapid prototyping allows for faster design iterations, reducing time-to-market and minimising financial risks. |
| Cost Management | Efficient use of materials and early flaw detection help organisations save on development expenses. |
Rapid prototyping represents a transformative approach in contemporary manufacturing that enables engineers and designers to swiftly create physical models directly from digital designs. Rapid prototyping techniques encompass methods that fabricate scale models using three-dimensional computer-aided design data, fundamentally changing how organisations develop and test product concepts.
At its core, rapid prototyping involves layer-by-layer material deposition techniques that allow manufacturers to produce intricate prototypes with unprecedented speed and precision. These advanced manufacturing processes enable quick production of physical models directly from solid digital representations, dramatically reducing the time between initial design conception and functional prototype evaluation.
The methodology integrates multiple advanced technologies, including:
Manufacturers across industries now leverage rapid prototyping techniques to accelerate product development cycles, reduce design iteration costs, and validate complex engineering concepts before full-scale production. This approach allows businesses to experiment, test, and refine designs with minimal financial risk and maximum engineering flexibility.
Rapid prototyping technologies encompass diverse manufacturing approaches that fundamentally differ in their material manipulation strategies, with additive and traditional methods representing two primary paradigms of prototype development. Additive manufacturing builds objects incrementally, while traditional methods remove material to create final components.
Additive manufacturing techniques, such as 3D printing, represent a revolutionary approach to prototype creation. These advanced technologies integrate multiple sophisticated processes like stereolithography and selective laser sintering, enabling intricate geometries that were previously impossible with conventional manufacturing methods. These techniques deposit material layer by layer, allowing unprecedented design complexity and material efficiency.
In contrast, traditional manufacturing methods like CNC machining follow a subtractive approach:
Each methodology offers unique advantages. Additive techniques excel in complex geometries and material efficiency, while traditional methods provide superior surface finish and material strength for certain applications. Engineers must carefully select the most appropriate technique based on specific project requirements, prototype complexity, and desired mechanical properties.
Rapid prototyping technologies have fundamentally transformed the product development landscape by enabling unprecedented speed in design iterations, allowing engineering teams to rapidly test and refine concepts with minimal time and resource investment. This revolutionary approach eliminates traditional barriers that historically slowed innovation, empowering designers to experiment more freely and efficiently.
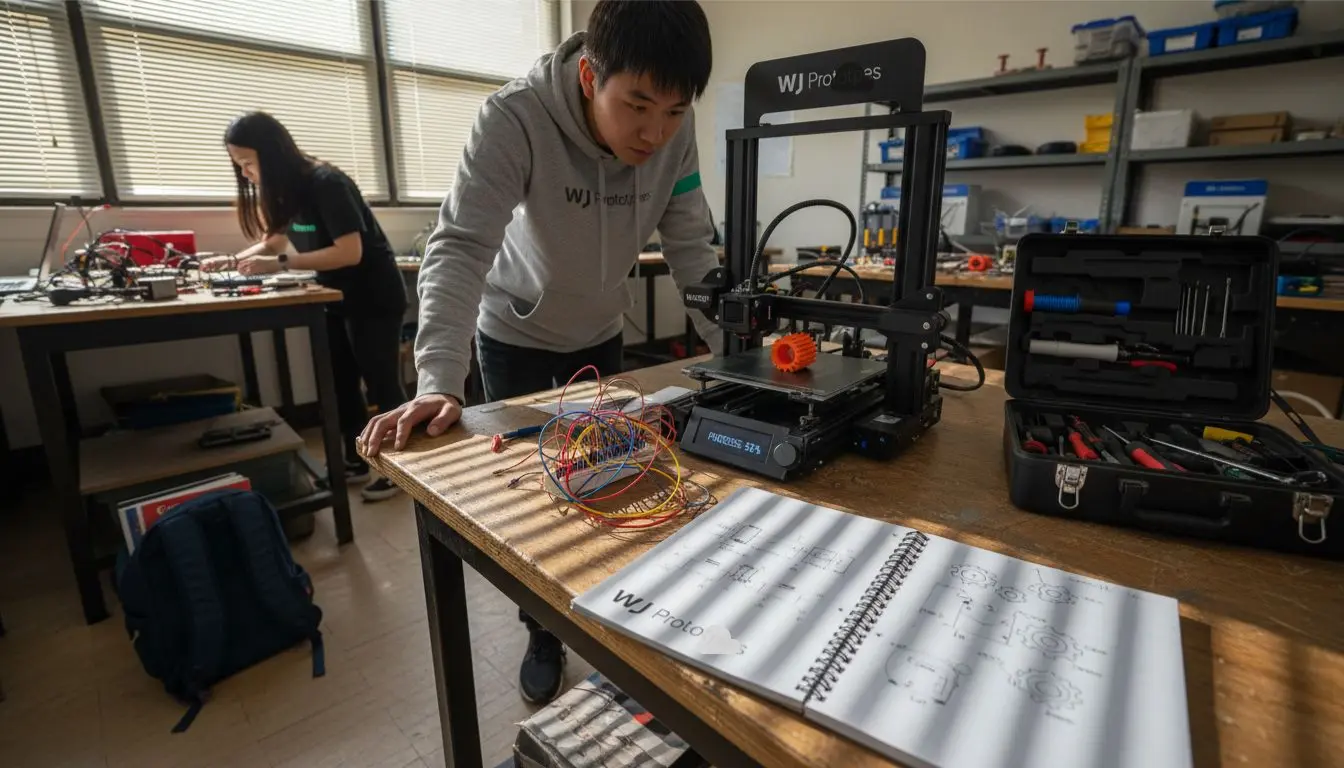
The core advantage of rapid prototyping lies in its ability to compress design cycles dramatically. Manufacturing organisations can now produce and evaluate multiple prototype iterations exponentially faster than conventional methods, reducing time-to-market and minimising financial risks associated with extended development processes. Iterative design becomes a streamlined, cost-effective strategy rather than a complex, time-consuming endeavour.
Key benefits of accelerated design iteration include:
Engineers and product developers can now leverage rapid prototyping techniques to create multiple design variations, test functional prototypes, and make informed decisions with unprecedented agility. This approach represents a paradigm shift in how organisations approach product development, transforming innovation from a linear process to a dynamic, responsive methodology.
Rapid prototyping technologies fundamentally transform cost management strategies in manufacturing by dramatically reducing material waste and development expenses. Traditional manufacturing approaches often involve substantial upfront investments and prolonged development cycles, whereas modern rapid prototyping enables organisations to minimise financial risks through more efficient, targeted product development processes.
Early detection of design flaws becomes a critical mechanism for reducing market risks and preventing expensive late-stage modifications. By identifying potential issues during initial prototype stages, companies can make precise adjustments before committing significant resources to full-scale production, thereby preventing potentially catastrophic financial setbacks.
Key financial advantages of rapid prototyping include:
Engineers and product managers can leverage rapid prototyping techniques to create more financially sustainable development strategies. This approach transforms product innovation from a high-risk endeavour into a calculated, manageable process that balances creative exploration with economic pragmatism.
Rapid prototyping has emerged as a transformative technology across multiple high-tech industries, enabling sophisticated manufacturers to produce complex components with unprecedented precision and efficiency. The aerospace, automotive, medical device, and electronics sectors have particularly benefited from these advanced manufacturing techniques, leveraging rapid prototyping to push the boundaries of traditional design and production limitations.

Medical device manufacturing and consumer electronics industries demonstrate remarkable innovation through quick product development and testing capabilities. These sectors utilise rapid prototyping to create intricate components, functional prototypes, and customised solutions that would be prohibitively expensive or technically impossible using conventional manufacturing methods.
Industry-specific applications include:
Engineers and product developers can now leverage industrial 3D printing techniques to accelerate innovation across diverse technological domains. This approach transforms conceptual designs into tangible, functional prototypes with remarkable speed and accuracy, revolutionising how organisations approach product development and technological advancement.
The article highlights the crucial challenge of accelerating design iteration while maintaining precision and minimising costs in modern manufacturing. If you are striving to reduce development time without compromising quality or risking expensive late-stage changes rapid prototyping is the answer. Through advanced techniques such as SLA, SLS, and CNC machining you can achieve fast production of intricate prototypes that allow you to test, refine, and validate your designs efficiently.
At WJ Prototypes, we understand these pain points and goals intimately. Our comprehensive services cover both additive and traditional manufacturing methods supported by a diverse range of materials and finishes. With decades of expertise spanning aerospace, automotive, medical, and electronics industries, we deliver high-quality, cost-effective rapid prototyping and low-volume manufacturing solutions tailored to your precision engineering needs. Rapidly transform your concepts into tangible models and accelerate your product development cycle by partnering with an ISO certified manufacturer committed to quick turnaround and global delivery. Explore how our rapid prototyping services can empower your innovation journey. Take the first step towards staying ahead in your market by requesting a quote or consulting our expert engineers today.
Rapid prototyping in precision manufacturing refers to techniques that allow for the quick creation of physical models from digital designs, primarily using layer-by-layer material deposition methods such as 3D printing and CNC machining. This approach significantly speeds up the production of prototypes for testing and evaluation.
Rapid prototyping reduces costs by minimising material waste, speeding up time-to-market, reducing tooling costs, and decreasing the expenses related to multiple design iterations. It allows for the early detection of design flaws, preventing costly modifications later in the development process.
Additive manufacturing excels in producing complex geometries and optimising material efficiency. Unlike traditional machining, it builds objects layer by layer, which allows for intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible to achieve through conventional means.
Rapid prototyping enables engineering teams to quickly create and test multiple design iterations, allowing for fast conceptualisation and more informed decision-making. This accelerates the overall product development cycle and enhances collaboration between design teams.
What Is Rapid Prototyping? Rapid Prototyping Explained by WJ Prototypes
Rapid Prototyping Vs Traditional Prototyping - A Complete Guide
Why Rapid Prototyping Matters - Key Benefits for Industry
Rapid Prototyping Guide | 5 Important Steps To Prototype Design & Manufacturing
How to Minimize Downtime: Efficient Diesel Injection Repairs