- Room 1807, Unit 9, Building 2, Shangxing Commercial Street, Shangde Road, Shangxing Community, Xinqiao Subdistrict, Bao'an District, Shenzhen City, China




Aerospace & UAV
WJ Prototypes is your 3D manufacturing partner from prototype to large scale production.
Consumer Electronics
New Product Introduction Solutions for Consumer Electronics.

Robotics & Automation
Need some assistance bringing your robotic device or parts from the sketch-board to reality?
Medical Devices
The medical industry needs high quality, dependable and safe parts and products.
Automotive
New Product Introduction Solutions for Automotive
Industrial Machinery
The main purpose of industrial prototyping is to take the product from drawings into the real world.


Most british and American aerospace companies now expect tangible prototypes in under ten days, pressuring engineers to rethink traditional timelines. Faster prototyping is vital when a single design delay can disrupt entire product launches or competitive bids. This quick guide shows how today's rapid prototyping services use advanced technologies, offer broad material choices, and support rigorous quality assurance, all to help you achieve reliable results and meet aggressive development schedules.
| Point | Details |
|---|---|
| Rapid Prototyping Overview | Rapid prototyping services expedite the transition from concept to tangible models, allowing for design validation and technical assessments. |
| Technology Varieties | Key methodologies such as SLA, SLS, and FDM offer diverse advantages depending on prototype requirements, including material properties and complexity. |
| Material Selection | Choosing the right materials is crucial, as it affects the quality, functionality, and performance of prototypes across various applications. |
| Quality Assurance | Rigorous quality control and compliance standards ensure high manufacturing precision and integrity throughout the prototyping process. |
Rapid prototyping services represent a sophisticated design and manufacturing approach that enables businesses to quickly transform conceptual ideas into tangible physical models. These services utilise advanced technologies to create early product models that simulate critical aspects of potential final products across multiple industries.
The core purpose of rapid prototyping involves creating functional representations that allow engineers and designers to validate design concepts, assess potential technical challenges, and refine product specifications before full-scale production. These services encompass various methodologies including 3D printing, CNC machining, injection moulding, and vacuum casting. Each technique offers unique advantages depending on the specific requirements of the prototype, such as material properties, complexity of design, and intended functional testing.
Modern rapid prototyping services provide significant strategic advantages for product development teams. By enabling faster iterations and reducing development cycles, companies can significantly compress time-to-market timelines. The approach supports multiple prototype variations - from basic conceptual models to highly detailed functional prototypes that closely mimic final product specifications. This flexibility allows businesses to experiment, learn, and adapt design concepts with minimal financial risk.
Expert Tip: When selecting a rapid prototyping service, prioritise providers offering multiple fabrication technologies to ensure maximum design flexibility and comprehensive prototype development capabilities.
Modern rapid prototyping harnesses a diverse range of advanced manufacturing technologies that enable engineers to transform digital designs into physical models with remarkable precision. Additive manufacturing techniques have revolutionised the prototyping landscape, offering multiple approaches to create complex geometries and functional prototypes across various industries.
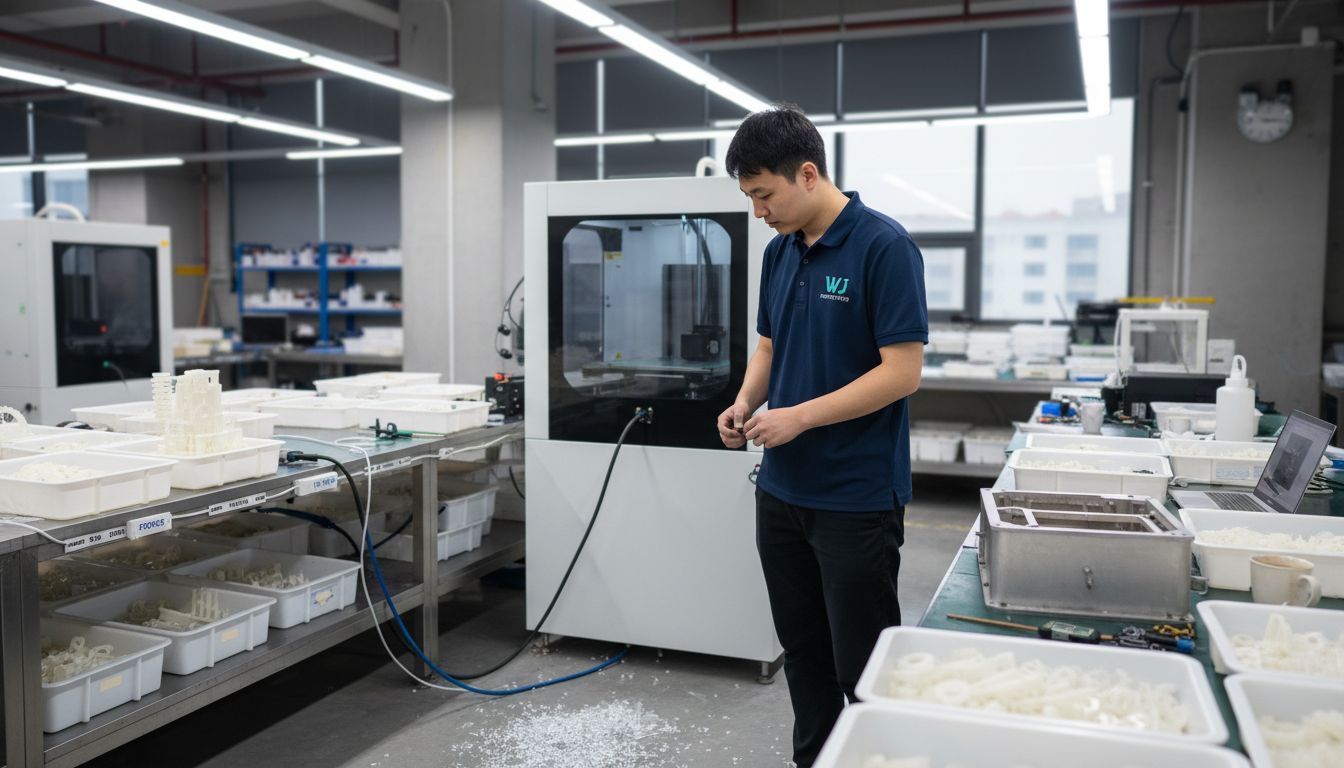

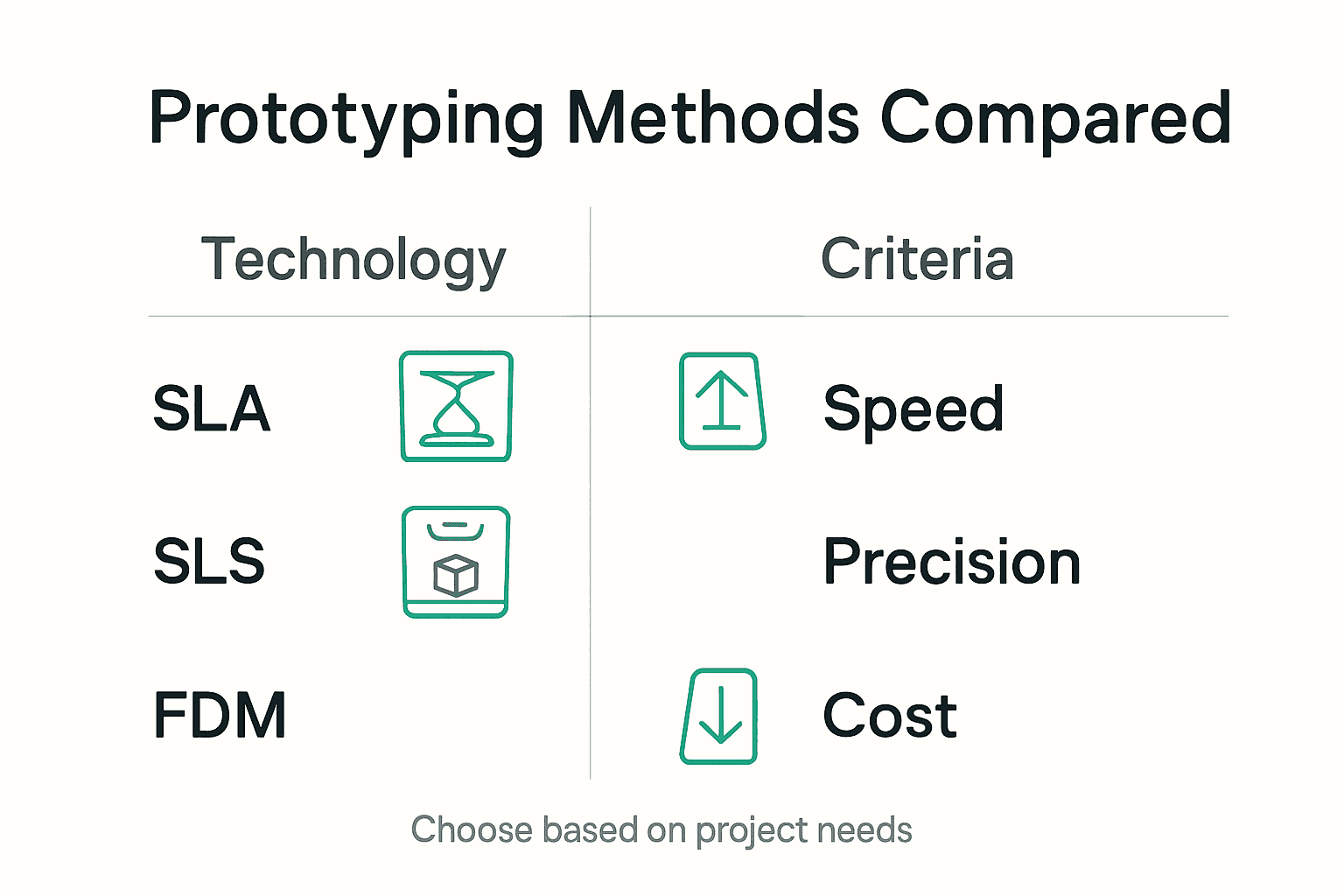
The primary technologies utilised in rapid prototyping include several key methodologies. Stereolithography (SLA) employs laser technology to cure liquid photopolymer resin layer by layer, producing highly detailed models with smooth surface finishes. Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) uses powdered materials like nylon or metal, which are selectively fused using high-powered lasers, enabling the creation of robust and complex geometric structures. Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) represents another critical technique, where thermoplastic filaments are extruded and deposited layer by layer to construct three-dimensional objects, offering excellent mechanical properties and material versatility.
Beyond traditional additive technologies, modern prototyping practices incorporate digital and extended reality tools that expand design exploration capabilities. These include advanced computer-aided design (CAD) software, virtual reality simulation environments, and hybrid manufacturing approaches that combine multiple fabrication techniques. Such technologies enable engineers to iterate designs rapidly, test functional requirements, and validate product concepts before committing to full-scale production, thereby minimising development costs and reducing time-to-market.
Here is a comparison of major rapid prototyping technologies and their typical applications:
| Technology | Most Suitable Materials | Key Advantage | Common Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stereolithography (SLA) | Photopolymer resins | Exceptional detail and smooth finishes | Medical models, fine prototyping |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Nylon, metal powders | Robust structures and design freedom | Aerospace parts, functional testing |
| Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM) | Thermoplastics (ABS, PLA, etc.) | Cost-effective for simple prototypes | Functional parts, rapid concept models |
| Digital Light Processing (DLP) | Photopolymer resins | High precision at micro-scale | Dental models, micro devices |
Expert Tip: Select prototyping technologies that align closely with your specific product requirements, considering factors like material properties, geometric complexity, and intended functional testing.
In rapid prototyping, precision and material selection are fundamental aspects that directly influence the quality, functionality, and performance of manufactured components. Digital fabrication technologies require meticulous material choices that balance mechanical properties, cost-effectiveness, and intended product requirements across diverse engineering applications.
Digital Light Processing (DLP) represents a cutting-edge additive manufacturing technique that exemplifies precision engineering. This advanced method utilises photopolymer resins and sophisticated light projection systems to create intricate microstructures with exceptional dimensional accuracy. The technology's precision depends critically on sophisticated system components like digital light engines and projection lenses, which enable engineers to produce complex geometries with tolerances measured in micrometres.
Material selection in rapid prototyping involves strategic considerations across multiple dimensions. Engineers must evaluate engineering-grade plastics, metals, and composite materials based on specific performance requirements. Key factors include mechanical strength, thermal resistance, chemical compatibility, and manufacturing complexity. Different prototyping technologies support varied material choices - from flexible thermoplastics in fused deposition modeling to robust metal alloys in selective laser sintering, each offering unique advantages for specific design challenges.
The following table summarises critical factors to consider when selecting materials for rapid prototyping:
| Selection Factor | Example Considerations | Impact on Prototype |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Strength | Resistance to applied loads | Determines durability |
| Thermal Resistance | Stability under temperature change | Affects operating environment |
| Chemical Compatibility | Exposure to chemicals, solvents | Influences long-term reliability |
| Manufacturing Complexity | Ease of processing, moulding | Affects turnaround and cost |
Expert Tip: Always conduct comprehensive material compatibility testing before finalising your prototype design, considering mechanical stress, environmental conditions, and intended functional requirements.
Rapid prototyping workflows integrate sophisticated digital processes that transform design concepts into tangible physical models with unprecedented efficiency. The turnaround process begins with comprehensive design assessment, where engineers meticulously evaluate project requirements, complexity, and technical specifications to develop an accurate production strategy.
The quoting mechanism involves a multi-dimensional analysis that considers several critical factors. Design Complexity emerges as a primary determinant of project timelines and costs, with intricate geometric structures requiring more advanced manufacturing techniques and precision tooling. Engineers examine material selections, prototype fidelity requirements, and anticipated production challenges to generate precise cost estimations. Prototyping timelines vary dramatically based on project specifications, ranging from several hours for digital mockups to multiple weeks for sophisticated physical prototypes.
Delivery processes in rapid prototyping emphasise continuous client communication and iterative refinement. Modern manufacturing workflows integrate digital technologies that enable real-time tracking, transparent progress reporting, and adaptive production strategies. Automated systems allow manufacturers to provide clients with precise estimated completion dates, material availability updates, and potential design modification recommendations. This approach ensures that clients remain informed throughout the entire prototyping journey, with flexibility to make critical adjustments without compromising overall project timelines.
Expert Tip:Prepare comprehensive design documentation and maintain open communication channels to expedite the quoting and delivery process, reducing potential misunderstandings and project delays.
Rapid prototyping quality assurance represents a comprehensive framework designed to ensure consistent, precise, and reliable manufacturing outcomes across diverse engineering applications. Strategic quality management approaches focus on delivering high standards aligned with rigorous industry expectations, integrating multiple verification mechanisms to maintain exceptional product integrity.
Compliance Standards in rapid prototyping encompass a multifaceted evaluation process that scrutinises every stage of product development. Engineers implement sophisticated quality control protocols that include dimensional accuracy assessments, material performance testing, and structural integrity verification. These systematic checks involve advanced measurement technologies like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), optical scanners, and precision microscopy to validate prototype specifications against original design parameters with microscopic precision.
Industrial quality assurance frameworks incorporate both internal and external validation processes. Manufacturers utilise statistical process control techniques, implementing continuous monitoring systems that track production variables such as material consistency, thermal stability, and geometric tolerances. International certification standards like ISO 9001 provide comprehensive guidelines that ensure manufacturers maintain consistent quality benchmarks, enabling transparent documentation, rigorous traceability, and systematic performance improvement strategies across manufacturing workflows.
Expert Tip: Develop a comprehensive quality checklist that includes both quantitative measurements and qualitative assessments to capture subtle variations that might impact prototype performance.
Comparative analysis of prototyping methods reveals significant variations in cost efficiency and production capabilities, with rapid prototyping emerging as a strategic solution for complex, low-volume manufacturing requirements. Traditional manufacturing approaches like conventional machining and investment casting often incur substantially higher production expenses compared to advanced additive manufacturing techniques.
Prototyping Technology Comparison involves evaluating multiple critical parameters beyond simple cost considerations. Different rapid prototyping methods such as Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM), Stereolithography (SLA), and polymer-based approaches demonstrate unique performance characteristics. FDM offers cost-effective solutions for straightforward geometric designs, while SLA provides superior precision at increased manufacturing expenses. Engineers must carefully assess project-specific requirements, balancing factors like geometric complexity, material properties, surface finish, and budget constraints.
Common mistakes in prototyping often stem from inadequate initial design planning or inappropriate technology selection. These errors can manifest as dimensional inaccuracies, material incompatibility, or unexpected functional limitations. Mitigation strategies include comprehensive digital simulation, iterative design refinement, and thorough prototype testing across multiple manufacturing scenarios. Virtual prototyping techniques and advanced computer-aided design (CAD) tools can help identify potential design vulnerabilities before physical production commences, thereby reducing overall development costs and minimising potential rework.
Expert Tip: Conduct a thorough cost-benefit analysis that considers not just immediate manufacturing expenses, but long-term design iteration and potential redesign requirements when selecting a prototyping approach.
The article highlights the critical challenge of achieving fast turnaround times without compromising precision and quality during rapid prototyping. If you are seeking to swiftly transform your design concepts into robust physical models while navigating complex requirements such as material selection, dimensional accuracy, and cost-efficiency, these are common pain points that demand a trusted manufacturing partner.
WJ Prototypes understands the urgency of reducing time-to-market and offers a comprehensive suite of advanced prototyping technologies including SLA, SLS, and CNC machining that align perfectly with your needs. Their expertise in precision engineering across aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors means you gain access to rapid iterations backed by rigorous quality assurance and ISO certification. By choosing WJ Prototypes you benefit from fast quoting tools, streamlined processes, and global delivery that keep your project on schedule.
Ready to overcome prototyping delays and costly mistakes with a reliable partner? Explore how rapid prototyping solutions from WJ Prototypes can accelerate your product development cycle today. Visit https://www.wjprototypes.com/ now to get an instant quote and start turning your ideas into reality with confidence.
Rapid prototyping is a design and manufacturing approach that quickly turns conceptual ideas into tangible physical models using advanced technologies such as 3D printing and CNC machining.
Key technologies include Stereolithography (SLA), Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), and Fused Deposition Modelling (FDM), each offering unique advantages depending on the prototype's material and complexity needs.
Material selection affects the quality and functionality of prototypes. Factors such as mechanical strength, thermal resistance, and chemical compatibility must be evaluated to ensure that the materials meet specific performance requirements.
Cost and turnaround time are influenced by design complexity, material choices, and the required fidelity of the prototype. Intricate designs typically require more advanced techniques, leading to longer timelines and higher costs.
Fast Prototyping Turnaround in China | Speed Up Product Development
Benefits of Rapid Prototyping for Precision Manufacturing in China
Why Rapid Prototyping Matters - Key Benefits for Industry
What Is Rapid Prototyping? Rapid Prototyping Explained by WJ Prototypes
How to Reduce Production Costs Effectively in 2025 – Spaceman